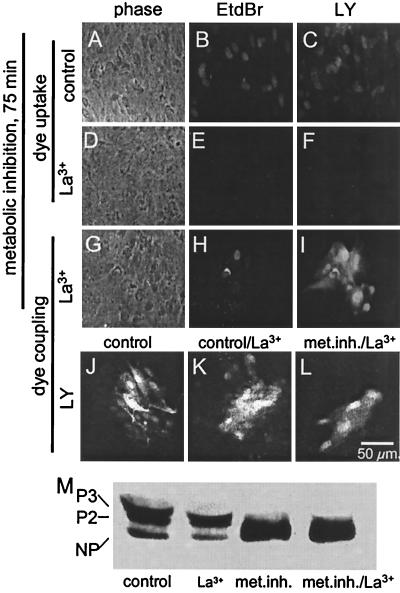
Figure 5.
Gap junctions between metabolically inhibited astrocytes are dye permeable at times when Cx43 is largely dephosphorylated. (A, D, and G) Phase views. (B, E, and H) EtdBr fluorescence. (C, F, I, and J–L) LY fluorescence. After 75 min metabolic inhibition, astrocytes showed EtdBr and LY uptake (B and C) that was prevented by extracellular application of 0.1 mM La3+ (E and F). In the same culture plate treated with La3+, EtdBr and LY coinjected into one cell diffused to several neighboring cells (H and I). Dye coupling in control medium (J) was not significantly different from dye coupling after 20 min exposure to 0.1 mM La3+ (K). Dye coupling of cells subjected to metabolic inhibition for 75 min with La3+ for the last 20 min was reduced (L). Western blot analysis of phosphorylation of Cx43 (M) showed that, under control conditions (lane control) and after treatment with La3+ for 20 min (lane La3+), the two phosphorylated forms (P3 and P2) were most abundant (compare with Fig. 6). Metabolic inhibition for 75 min (lane met. inh.) caused marked dephosphorylation that was not affected by addition of La3+ added for the last 20 min (lane met. inh./La3+).