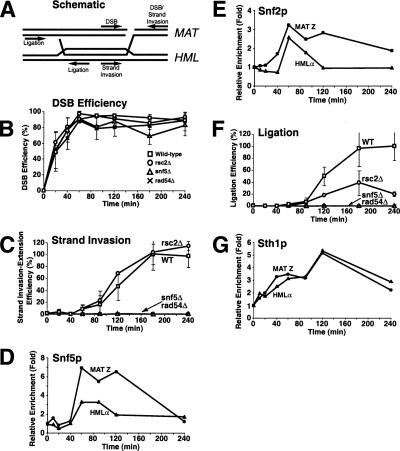
Figure 5.
rsc and swi/snf are defective at distinct steps of HR repair. (A) Schematic diagram of an HR intermediate during mating-type switching. Primers used to monitor DSB, strand invasion-extension, and completion of repair are indicated. (B,C,F) DSBs were induced in wild-type (BLY747), rsc2Δ (BLY784), snf5Δ (BLY786), and rad54Δ (BLY804) strains as described in Figure 4. Genomic DNA was isolated at the indicated time points and monitored by quantitative real-time PCR analysis for efficiency of DSB formation (B), primer extension (C), and completion of repair (F) (see Supplemental Material for details). Primer extension and completion of repair were arbitrarily set at 100% for the highest wild-type level. All values were normalized to an ACT1 internal control. The values are the averages of three independent experiments except for experiments carried out in snf5Δ and rad54Δ strains, which were each done twice. Error bars indicate one standard deviation. (D,E,G) Chromatin was also isolated from wild-type (BLY747) strains at the indicated time points and immunoprecipitated with anti-Snf5p, anti-Snf2p, or anti-Sth1p antibodies, followed by quantitative real-time PCR analysis as described in Figure 3.