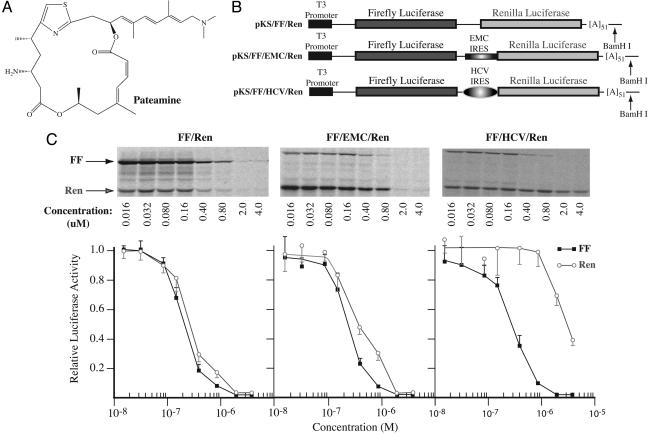
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of eukaryotic translation by pateamine. (A) Chemical structure of pateamine. (B) Schematic diagram of bicistronic constructs used to assess translation inhibition by pateamine. (C) Titration of pateamine in Krebs extracts programmed with bicistronic mRNAs. Translations were performed in the presence of the indicated amounts of pateamine and at a final mRNA and K+ concentration of 5 μg/ml and 100 mM, respectively. Firefly and renilla luciferase activity (RLU) were measured on a Berthold Technologies (Bad Wildbad, Germany) Lumat LB 9507 luminometer. Control translation reactions contained equivalent amounts of DMSO (data not shown). (Upper) Representative autoradiograph from an experiment performed with [35S]methionine. After separation of protein products on 10% polyacrylamide/SDS gels, the gels were treated with EN3Hance (PerkinElmer) dried, and exposed to X-Omat (Kodak) film. (Lower) Graphical representation of the effects of pateamine on translation of bicistronic mRNAs in Krebs extracts. The obtained luciferase activities were normalized to the activity obtained in the absence of compound (which was set at one). Each data point represents the average of three to seven translations, and the standard error of the mean is presented.