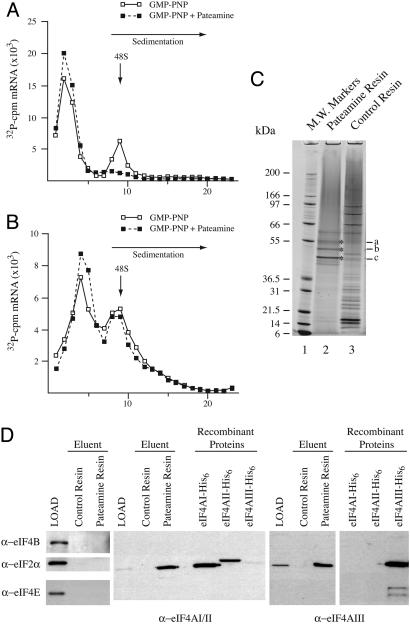
Fig. 2.
Pateamine inhibits ribosome recruitment. (A and B) 32P-labeled CAT and HCV/Ren mRNAs were incubated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate in the presence of 1 mM GMP-PNP or 1 mM GMP-PNP and 10 μM pateamine. After centrifugation (SW40; 39,000 rpm/3.5 h), fractions from each sucrose gradient were collected by using a Brandel (Bethesda, MD) Tube Piercer connected to an ISCO fraction collector and were individually counted. Total counts recovered from each gradient and the percent mRNA bound in 48S complexes were: (A) CAT mRNA/GMP-PNP (64,430 cpm, 21% binding) and CAT mRNA/GMP-PNP+pateamine (62,713 cpm, <0.7% binding), and (B) HCV/Ren mRNA/GMP-PNP (57,844 cpm, 7% binding) and HCV/Ren mRNA/GMP-PNP+pateamine (56,113 cpm, 6% binding). (C) eIF4A is specifically retained on a pateamine-Sepharose affinity matrix. Pateamine was coupled to epoxy-activated Sepharose, and total HL-60 cell extracts were loaded onto pateamine or control resin, washed with 0.1% Triton X-100 in 10 mM PBS, and eluted in SDS/PAGE sample buffer. Proteins were fractionated on a 4-12% polyacrylamide/SDS gel and stained with colloidal Coomassie blue. (D) Immunoblots of HL-60 extract (LOAD) and eluents from control- and pateamine-affinity resins. The antibodies used in the immunoblots are indicated. Recombinant eIF4AI, eIF4AII, and eIF4AIII proteins were used to assess antibody specificity. Recombinant eIF4AII has a higher molecular mass than recombinant eIF4AI due to additional vector-derived sequences.