Figure 5.
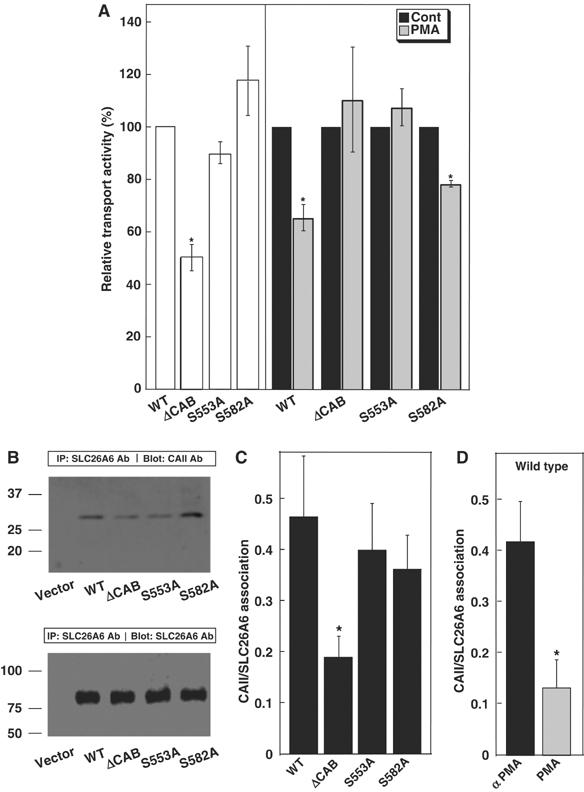
Identification of the PKC-responsive site in the SLC26A6 C-terminal region. (A) HEK293 cells transfected with WT SLC26A6 cDNA or the indicated mutants were switched from Cl−-containing to Cl−-free Ringer's buffer and the process was repeated after 10 min incubation with 200 nM PMA. Open bars indicate Cl−/HCO3− exchange activity, relative to WT SLC26A6 for samples not treated with PMA. Transport activity before (black bars) and after (grey bars) PMA treatment was normalized to the activity of associated with each cell type, under control conditions. *P<0.05, n=4. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with vector alone, WT, ΔCAB, S553A or S582A SLC26A6, as indicated. Cell lysates wre immunoprecipitated with anti-SLC26A6 antibody and immunoprecipitates were probed for associated CAII on immunoblots probed with anti-CAII antibody (upper panel). The amount of SLC26A6 present in each sample was assessed on parallel blots probed with anti-SLC26A6 antibody (lower panel). (C) Immunoprecipitation of CAII with SLC26A6 variants was calculated as (amount of CAII/amount of SLC26A6). (D) The effect of PMA on CAII/SLC26A6 association was measured as in panels B and C, except that SLC26A6-expressing cells were incubated with either 200 nM αPMA (black bar) or PMA (grey bar) for 1 h prior to cell lysis. *P<0.05.
