Figure 8.
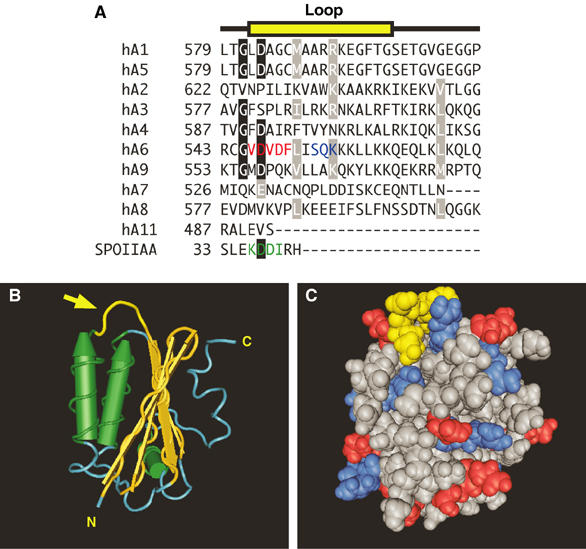
Structural basis for regulation of SLC26A6 by PKC: the STAS domain. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of the amino-acid sequence of a surface loop (yellow) in the STAS domain of human (h) SLC26A1–SLC26A11 (hA1–hA11) and the sporulation-specific sigma factor of B. subtilis, SPOIIAA. Conserved residues (black boxes) and conservative replacements (gray boxes) are indicated. The sequence for loop residues in SPOIIAA is highlighted (green). The CAII-binding site (red) and consensus PKC phosphorylation site (blue) are present only in SLC26A6. (B) Structural model of the STAS domain from SPOIIAA (PDB code 1BUZ) (Kovacs et al, 1998). Yellow structure highlighted with an arrow indicates the position of the variable loop between helix 1 and strand 3 (corresponding to the sequence highlighted in yellow in panel A). Cylinders represent α-helices and arrows represent β-sheets. N, amino-terminus; C, carboxyl-terminus. (C) Space-filling model of SPOIIAA oriented as in panel B. Loop region residues are yellow, while positive and negative residues are blue and red, respectively. Structures were rendered with Cn3D software.
