Figure 4.
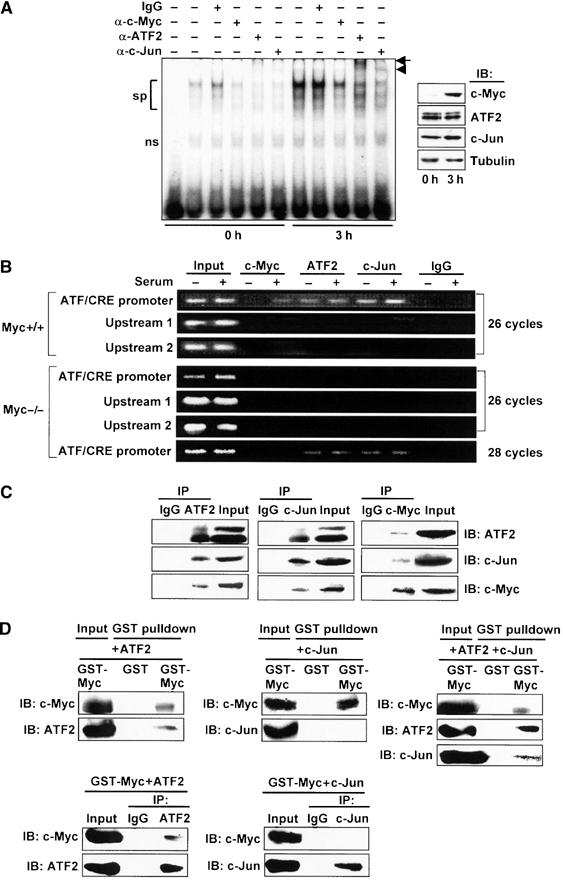
Binding of ATF2/c-Jun to ATF/CRE motif and c-Myc recruitment to the ATF3 gene promoter in response to serum. (A) Nuclear extract from wild-type cells serum starved or serum stimulated for 3 h was assayed for gel shift using radiolabeled DNA probe from −102 to −73 containing the ATF/CRE motif. From left: probe only, extract from the starved or serum-stimulated cells with or without the indicated antibodies. sp: specific bands; ns: nonspecific bands; arrow: supershift by anti-ATF2 antibody; arrowhead: supershift by anti-c-Jun antibody. In the inset, the expressions of c-Myc, ATF2, and c-Jun proteins were measured by Western blot. (B) Upper panel: Serum-starved or serum-stimulated wild-type cells were crosslinked with formaldehyde, and ChIP assay was performed using anti-c-Myc, anti-ATF2, or anti-c-Jun antibodies. ATF/CRE promoter region from −120 to +30, upstream region 1 from −370 to −120, and upstream region 2 from −570 to −370 were amplified by 26 cycles of PCR. Lower panel: c-myc-deficient cells were also subjected to ChIP assay, as above. ATF/CRE promoter region was also amplified by 28 cycles of PCR. (C) Whole-cell extracts from 293T cells overexpressing c-Myc, ATF2, and c-Jun were immunoprecipitated as in Materials and methods using anti-ATF2 (left panel), anti-c-Jun (middle panel), or anti-c-Myc antibody (right panel), respectively, and the resulting immune complex was subjected to Western blot analysis. Input was 10% of total. (D) Recombinant GST-c-Myc was mixed with ATF2 (upper left panel) or c-Jun alone (upper middle panel), or together (upper right panel), and GST pulldown assay was performed as in Materials and methods. In the lower panel, binding of GST-c-Myc with ATF2 or c-Jun was inversely assayed by immunoprecipitation using anti-ATF2 (lower left panel) or anti-c-Jun antibody (lower right panel), respectively. Input was 10% of total.
