Abstract
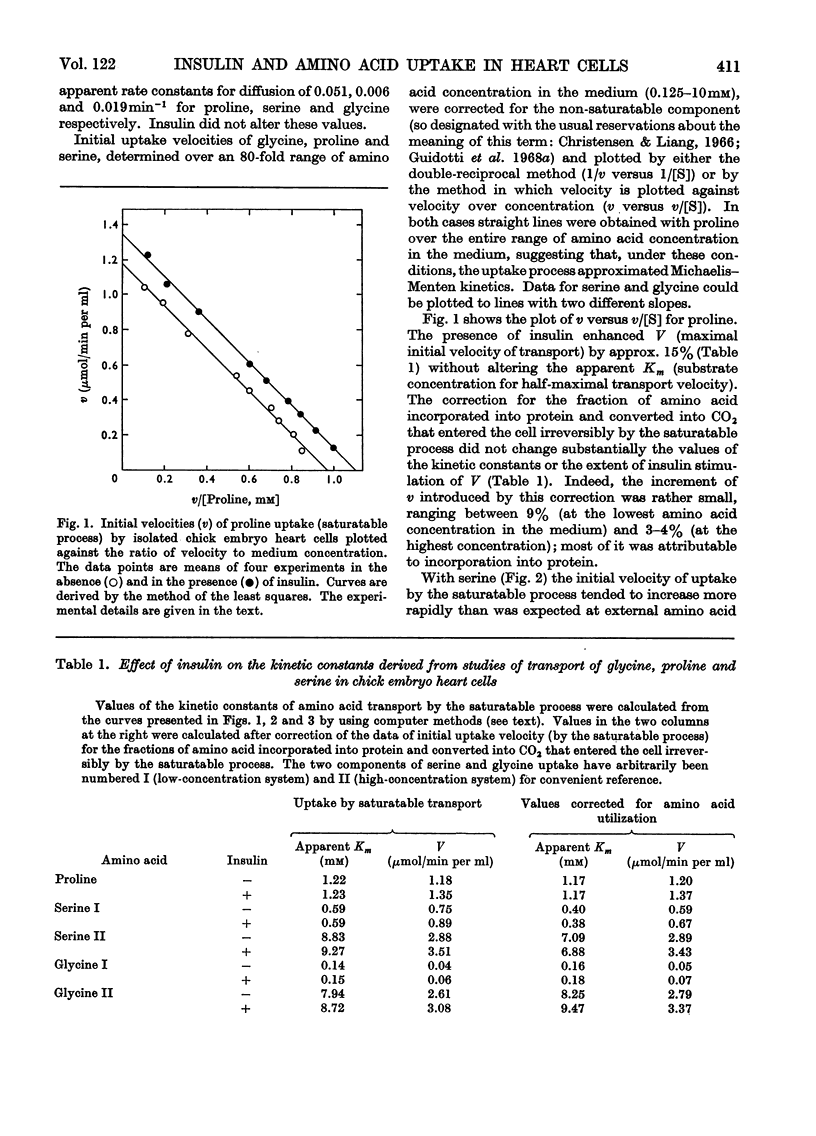
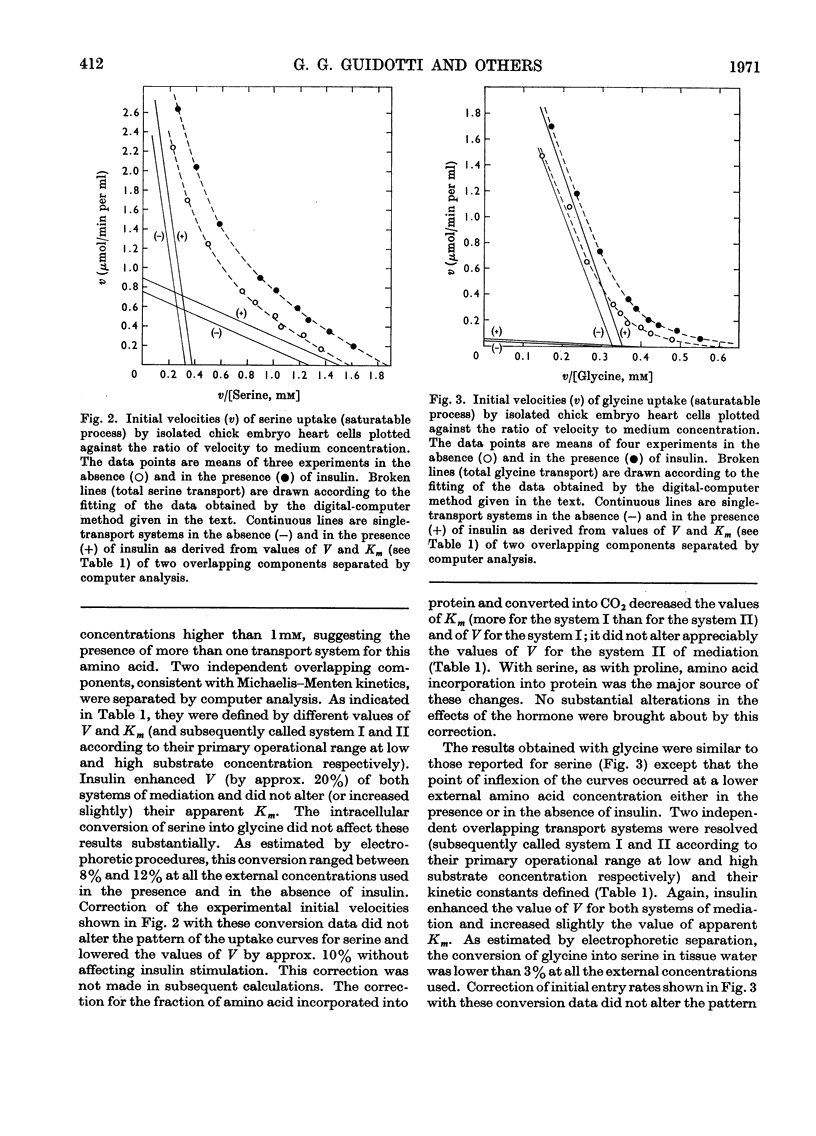
1. Isolated chick embryo heart cells were used to investigate the mode of action of insulin on the transport of three naturally occurring amino acids: l-proline, l-serine and glycine. Initial velocities of uptake were measured over a period of 5min with an 80-fold range of amino acid concentration. Corrections for amino acid diffusion, incorporation into protein and conversion into carbon dioxide were introduced. 2. The uptake processes approximated Michaelis–Menten kinetics within definite ranges of amino acid concentrations. A single transport system for proline and at least two transport systems for serine and glycine were detected. 3. The kinetic effects of insulin on transport systems for the amino acids tested were consistent with an acceleration of the maximal velocity of the process, without substantial changes in substrate concentration for half-maximal transport velocity. 4. These hormonal effects were not essentially altered by the corrections for amino acid incorporation into protein and conversion into carbon dioxide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKEDO H., CHRISTENSEN H. N. Nature of insulin action on amino acid uptake by the isolated diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:118–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Liang M. Transport of diamino acids into the Ehrlich cell. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5542–5551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWD J. E., RIGGS D. S. A COMPARISON OF ESTIMATES OF MICHAELIS-MENTEN KINETIC CONSTANTS FROM VARIOUS LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:863–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Albrecht I., Rosenberg L. E. Insulin stimulation of amino acid uptake in rat diaphragm. Relationship to protein sythesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1846–1853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Borghetti A. F., Gaja G., Loreti L., Ragnotti G., Foà P. P. Amino acid uptake in the developing chick embryo heart. The effect of insulin on alpha-aminoisobutyric acid accumulation. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):565–574. doi: 10.1042/bj1070565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Gaja G., Loreti L., Ragnotti G., Rottenberg D. A., Borghetti A. F. Amino acid uptake in the developing chick embryo heart. The effect of insulin on glycine and leucine accumulation. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):575–580. doi: 10.1042/bj1070575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Lüneburg B., Borghetti A. F. Amino acid uptake in isolated chick embryo heart cells. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;114(1):97–105. doi: 10.1042/bj1140097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman R. E., Albrecht I., Rosenberg L. E. Identification and analysis of multiple glycine transport systems in isolated mammalian renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5566–5571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman R. E., Rosenberg L. E. Amino acid transport by isolated mammalian renal tubules. II. Transport systems for L-proline. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4494–4498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L., WOOL I. G. INSULIN AND INCORPORATION OF AMINO ACIDS INTO PROTEIN OF MUSCLE. 1. ACCUMULATION AND INCORPORATION STUDIES WITH THE PERFUSED RAT HEART. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:202–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0890202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchester K. L. The control by insulin of amino acid accumulation in muscle. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):457–465. doi: 10.1042/bj1170457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter C. G., Christensen H. N. Contrasts in neutral amino acid transport by rabbit erythrocytes and reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3594–3600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G., Castles J. J., Moyer A. N. Regulation of amino acid accumulation in isolated rat diagphragm: effect of puromycin and insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 13;107(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


