Fig. 1. Construction of high-body-order ACE features.
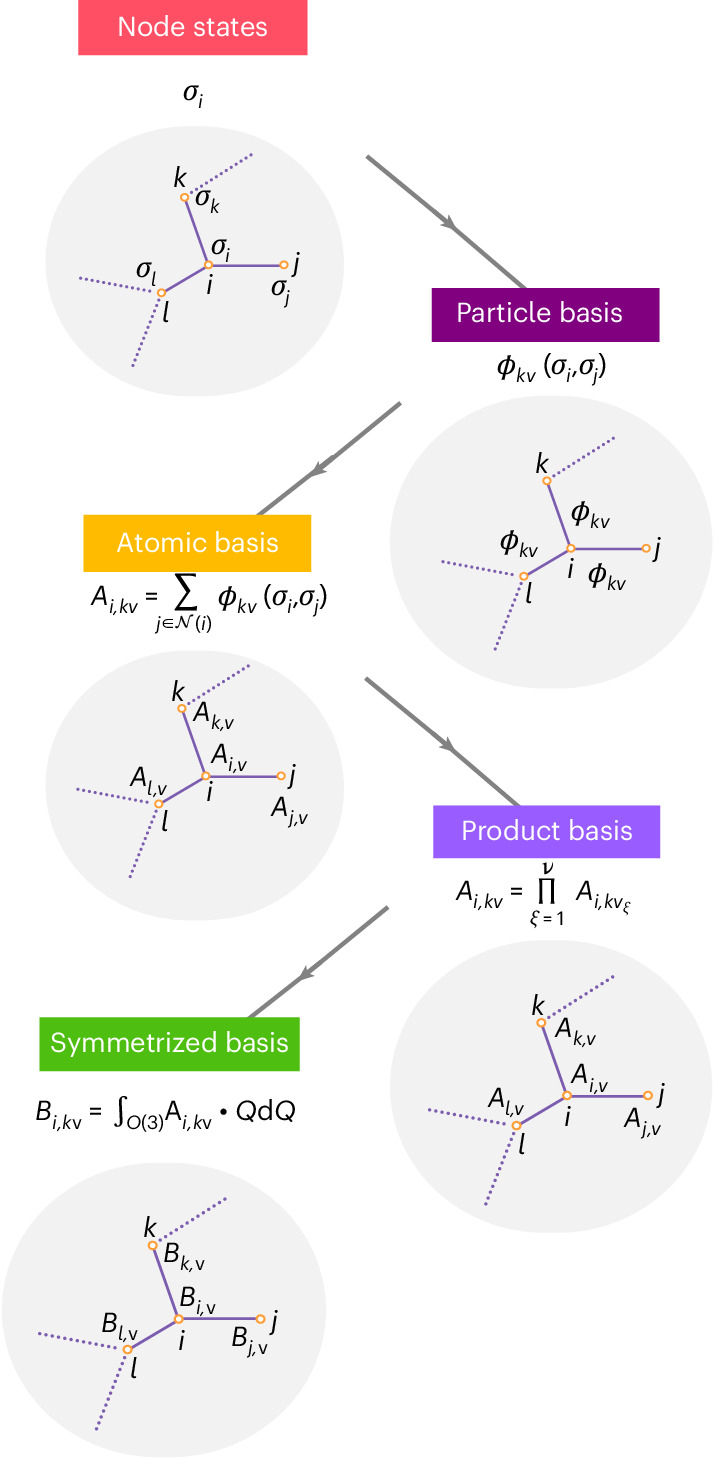
First a neighbourhood graph is constructed with each node labelled with its state. The one-particle basis is then computed for each edge. After that, a pooling operation is performed to create permutation-invariant A functions of semi-local environments. To construct higher-body-order features, the product basis is formed by taking the tensor products of all coupled indices of the A functions. Finally, to create equivariant messages, the B basis is formed by first specifying the required equivariance and then evaluating the corresponding symmetrization integral. The invariant B basis is shown here.
