Abstract
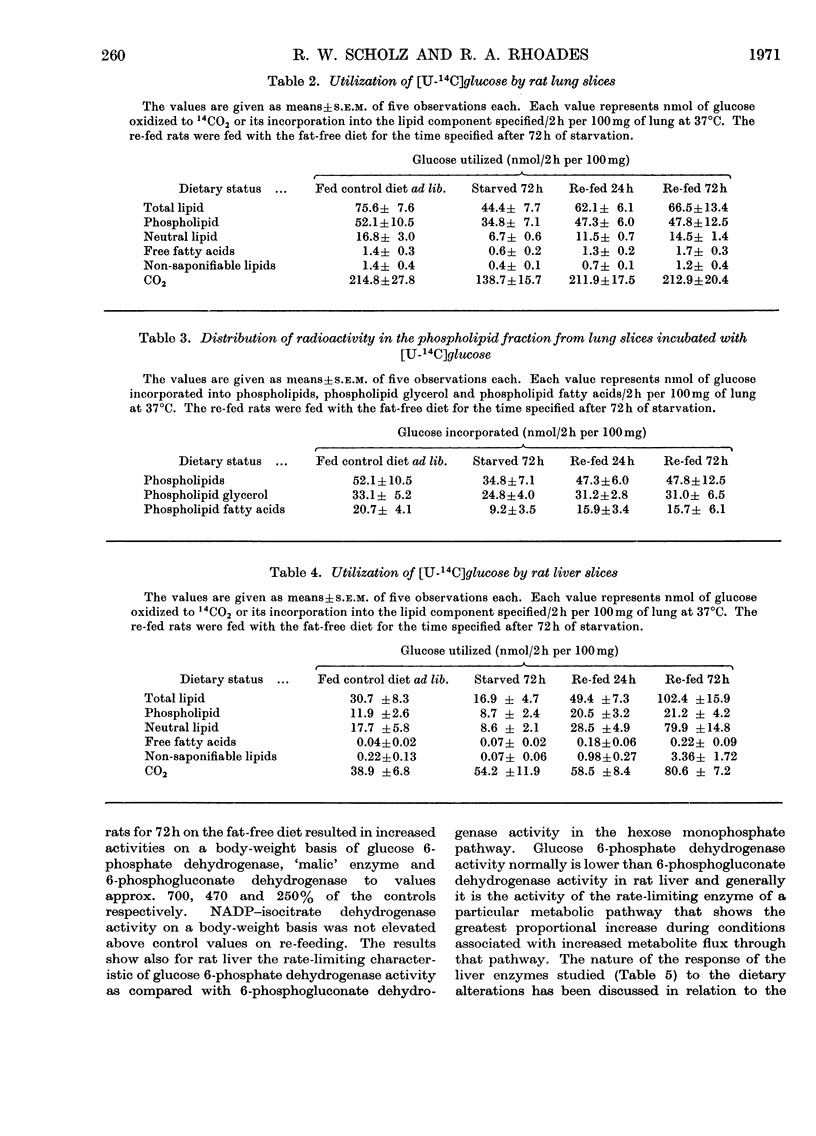
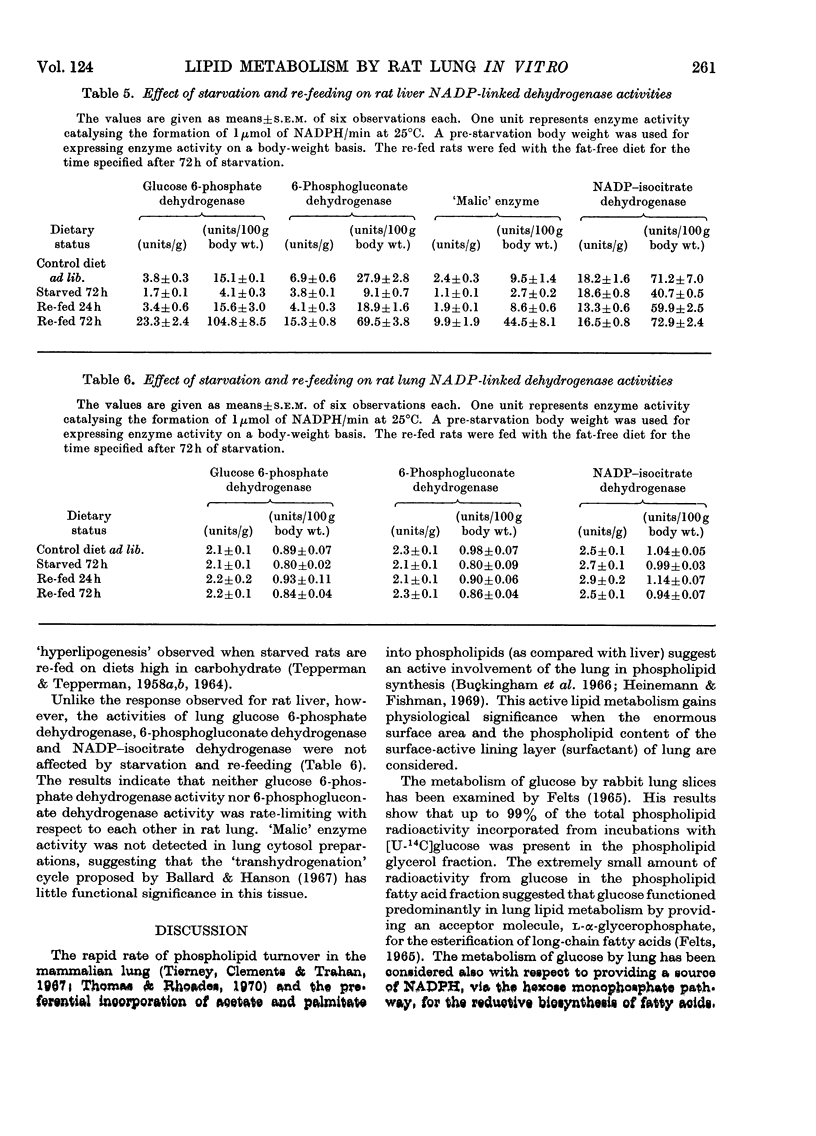
1. The incorporation of [U-14C]glucose into several lipid components of lung and liver slices, and the activities of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.44), `malic' enzyme (EC 1.1.1.40) and NADP–isocitrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.42) of the cell cytosol were examined in normal, starved and re-fed rats. 2. Lipogenesis and the activities of these enzymes in liver were decreased markedly in rats starved for 72h. Re-feeding starved rats on a fat-free diet for 72h resulted in the well documented hyperlipogenic response in liver, particularly in its ability to convert glucose into neutral lipid, and increased activities of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, `malic' enzyme and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase to values approx. 700, 470 and 250% of controls respectively. 3. Approx. 70% of the total label in lung lipids was present in the phospholipid fraction. Hydrolysis of lung phospholipids revealed that lipogenesis from glucose was considerable, with approx. 40% of the total phospholipid radioactivity present in the fatty acid fraction. 4. Incorporation of glucose into total lung lipids was decreased by approx. 40% in lung slices of starved rats and was returned to control values on re-feeding. Although phospholipid synthesis from glucose was decreased in lung slices of starved rats, the decrease proportionally was greater for the fatty acid fraction (approx. 50%) as compared with the glycerol fraction (approx. 25%). 5. The activities of lung glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase and NADP–isocitrate dehydrogenase were not affected by the dietary alterations. `Malic' enzyme activity was not detected in lung cytosol preparations. 6. The results are discussed in relation to the surface-active lining layer (surfactant) of the lung.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLMANN D. W., HUBBARD D. D., GIBSON D. M. FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DURING FAT-FREE REFEEDING OF STARVED RATS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:63–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORTZ W. M., LYNEN F. THE INHIBITION OF ACETYL COA CARBOXYLASE BY LONG CHAIN ACYL COA DERIVATIVES. Biochem Z. 1963 Aug 14;337:505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUHLER D. R. A simple scintillation counting technique for assaying C1402 in a Warburg flask. Anal Biochem. 1962 Nov;4:413–417. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman D. E., Brown R. E., Davis C. L. Pathways of fatty acid synthesis and reducing equivalent generation in mammary gland of rat, sow, and cow. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Sep;140(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham S., Heinemann H. O., Sommers S. C., McNary W. F. Phospholipid synthesis in the large pulmonary alveolar cell. Its relation to lung surfactants. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jun;48(6):1027–1041. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey J. A., Porter J. W. The effect of palmityl coenzyme A on pigeon liver fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3512–3516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAVARGER P., GERLACH J. Recherches sur la synthèse des graisses a partir d'acétate ou de glucose. I. Vitesse d'incorporation de l'acétate dans les acides gras de la souris amaigrie. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1955;13(2):91–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELTS J. M. CARBOHYDRATE AND LIPID METABOLISM OF LUNG TISSUE IN VITRO. Med Thorac. 1965;22:89–99. doi: 10.1159/000386167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLATT J. P., BALL E. G. STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF ADIPOSE TISSUE. XV. AN EVALUATION OF THE MAJOR PATHWAYS OF GLUCOSE CATABOLISM AS INFLUENCED BY INSULIN AND EPINEPHRINE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:675–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faridy E. E. Effect of food and water deprivation on surface activity of lungs of rats. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Oct;29(4):493–498. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.29.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fábry P., Kleinfeld R., Tepperman H. M., Tepperman J. Effect of diet and insulin on the morphology and TPNH generating enzyme activities of rat adipose tissue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Feb;133(2):577–581. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., McLEAN P. Further studies on the properties and assay of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase of rat liver. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):400–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0550400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., McLEAN P. Levels of enzymes of the direct oxidative pathway of carbohydrate metabolism in mammalian tissues and tumours. Biochem J. 1954 Jan;56(1):171–175. doi: 10.1042/bj0560171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbagni R., Coppo F., Grassini G., Cardellino G. Effects of lipide loading and fasting on pulmonary surfactant. Respiration. 1968;25(6):458–464. doi: 10.1159/000192580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARPER A. E. Amino acid balance and imbalance. I. Dietary level of protein and amino acid imbalance. J Nutr. 1959 Jul 10;68(3):405–418. doi: 10.1093/jn/68.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINEMANN H. O. Free fatty acid production by rabbit lung tissue in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1961 Oct;201:607–610. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.4.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J., AHRENS E. H., Jr The separation of complex lipide mixtures by the use of silicic acid chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):311–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan W. R., Jr, Said S. I., Banerjee C. M. Metabolism of pulmonary phospholipids in normal lung and during acute pulmonary edema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Dec;94(6):938–947. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.94.6.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jomain M., Hanson R. W. Dietary protein and the control of fatty acid synthesis in rat adipose tissue. J Lipid Res. 1969 Nov;10(6):674–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAUS M. H., CLEMENTS J. A., HAVEL R. J. Composition of surface-active material isolated from beef lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Nov 15;47:1858–1859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.11.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAUS M., REISS O. K., TO OLEY W. H., PIEL C., CLEMENTS J. A. Alveolar epithelial cell mitochondria as source of the surface-active lung lining. Science. 1962 Sep 7;137(3532):750–751. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3532.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley T. F. Rapid assay of labeled free fatty acids in mixtures of labeled lipids. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):799–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDS W. E. Metabolism of glycerolipides; a comparison of lecithin and triglyceride synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):883–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveille G. A., Hanson R. W. Adaptive changes in enzyme activity and metabolic pathways in adipose tissue from meal-fed rats. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jan;7(1):46–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveille G. A., O'Hea E. K. Influence of periodicity of eating on energy metabolism in the rat. J Nutr. 1967 Dec;93(4):541–545. doi: 10.1093/jn/93.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S., Russell J. C., Taylor A. W. Determination of glycogen in small tissue samples. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Feb;28(2):234–236. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.2.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASORO E. J., CHAIKOFF I. L., CHERNICK S. S., FELTS J. M. Previous nutritional state and glucose conversion to fatty acids in liver slices. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):845–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGILVERY R. W., MOKRASCH L. C. Purification and properties of fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):909–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASR K., HEINEMANN H. O. LIPID SYNTHESIS BY RABBIT LUNG TISSUE IN VITRO. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jan;208:118–121. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novello F., Gumaa J. A., McLean P. The pentose phosphate pathway of glucose metabolism. Hormonal and dietary control of the oxidative and non-oxidative reactions of the cycle in liver. Biochem J. 1969 Mar;111(5):713–725. doi: 10.1042/bj1110713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hea E. K., Leveille G. A. Lipogenesis in isolated adipose tissue of the domestic chick (Gallus domesticus). Comp Biochem Physiol. 1968 Jul;26(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(68)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande S. V., Mead J. F. Inhibition of enzyme activities by free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6180–6185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury-Murphy S., Rubinstein D., Beck J. C. Lipid metabolism in lung slices. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):988–992. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratman S. L., Conejeros M. Resistance to experimental bacterial infection among different stocks of rats. Lab Anim Care. 1969 Oct;19(5):742–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN H. M., TEPPERMAN J. PATTERNS OF DIETARY AND HORMONAL INDUCTION OF CERTAIN NADP-LINKED LIVER ENZYMES. Am J Physiol. 1964 Feb;206:357–361. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN H. M., TEPPERMAN J. The hexosemonophosphate shunt and adaptive hyperlipogenesis. Diabetes. 1958 Nov-Dec;7(6):478–485. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.6.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Effects of antecedent food intake pattern on hepatic lipogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):55–64. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMBROPOULOS E. G. FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS BY SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF LUNG TISSUE. Science. 1964 Nov 27;146(3648):1180–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3648.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYLER W. S., PEARSE A. G. OXIDATIVE ENZYMES OF THE INTERALVEOLAR SEPTUM OF THE RAT. Thorax. 1965 Mar;20:149–152. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepperman J., Tepperman H. M. Gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis and the Sherringtonian metaphor. Fed Proc. 1970 May-Jun;29(3):1284–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T., Jr, Rhoades R. A. Incorporation of palmitate-1-14C into lung tissue and "alveolar" lecithin. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1535–1538. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney D. F., Clements J. A., Trahan H. J. Rates of replacement of lecithins and alveolar instability in rat lungs. Am J Physiol. 1967 Sep;213(3):671–676. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.3.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIELAND O., WEISS L. INHIBITION OF CITRATE-SYNTHASE BY PALMITYL-COENZYME A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Sep 10;13:26–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. M., Anhalt B., Beck J. C., Rubinstein D. Lipid metabolism in rabbit lungs. Can J Biochem. 1970 Feb;48(2):170–177. doi: 10.1139/o70-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG J. W., SHRAGO E., LARDY H. A. METABOLIC CONTROL OF ENZYMES INVOLVED IN LIPOGENESIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochemistry. 1964 Nov;3:1687–1692. doi: 10.1021/bi00899a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


