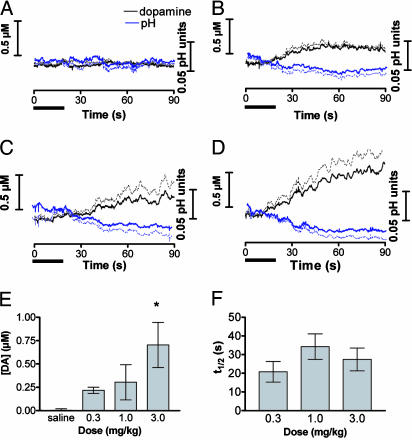
Fig. 4.
Dopamine changes caused by i.v. cocaine infusion. Rats were given saline and cocaine in cumulative doses (n = 6 rats). Error bars represent SEM. The solid bar beneath each graph indicates the infusion time. (A-D) Average time course of dopamine (black lines) and pH (blue lines) changes for saline (A) and 0.3 (B), 1.0 (C), and 3.0 (D) mg/kg cocaine. The dashed lines above the dopamine trace and below the pH trace represent the SEM. (E) Average changes in dopamine concentration measured for 10 s beginning 60 s after the infusion (one-way ANOVA, Duncan post hoc test: *, P < 0.05 versus saline). (F) Time for dopamine concentration to reach one half of its maximum value after cocaine infusion.