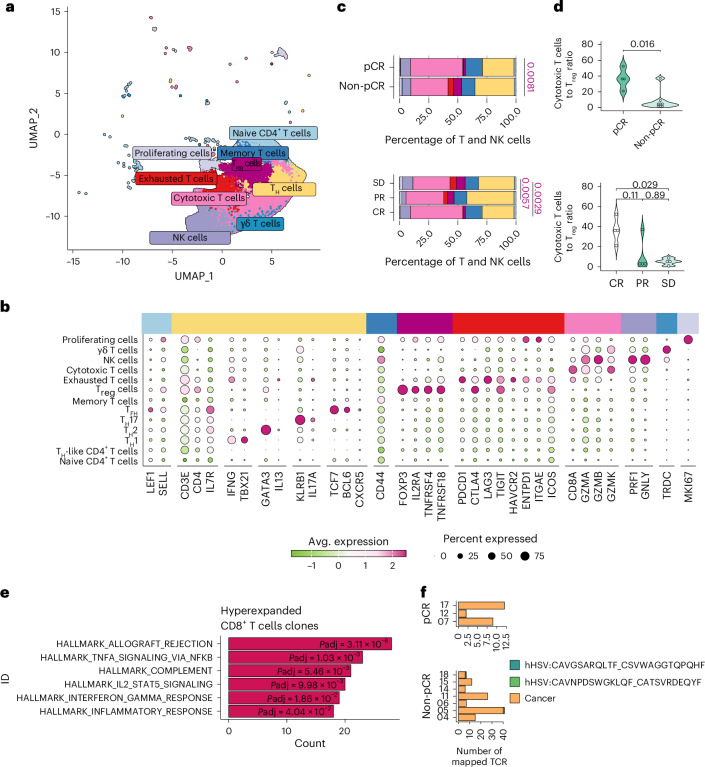
Fig. 4. T-VEC favors the expansion of hyper-expanded, cytotoxic T cell clones.
a, UMAP presenting post-treatment T cells (eight clusters) and NK cells (one cluster) b, Bubble plot indicating the average (Avg.) expression of selected marker genes in each cell cluster, including a subclassification of T helper cells (13 clusters). c, Bar plots presenting the composition of T cells. The colors reflect the ones of the immune cell clusters of a, split by pathological (pCR versus non-pCR) and clinical (CR, PR and SD) response (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test; statistical significance determined with P < 0.05). d, Violin plot demonstrating the ratio of cytotoxic T cells and Treg cells. Cytotoxic T cell/Treg ratio of patients according to pathological response (pCR (n = 4) and non-pCR (n = 8)) and clinical response (CR (n = 4), PR (n = 4) and SD (n = 4)) (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test; statistical significance determined with P < 0.05). e, Bar plots presenting terms from the MSigDB Hallmarks database that were enriched in hyper-expanded T cell clones. Terms are ranked by the total number of genes overlapping differentially expressed genes and adjusted P values are indicated (enricher one-sided hypergeometric test with false discovery rate correction; Benjamini–Hochberg)77. The universe is defined by all detected genes in the T cell subset. f, Bar plots displaying the number of T cell clones aligned to the MacPAS-TCR database according to human HSV- and cancer-associated TCRs.