Abstract
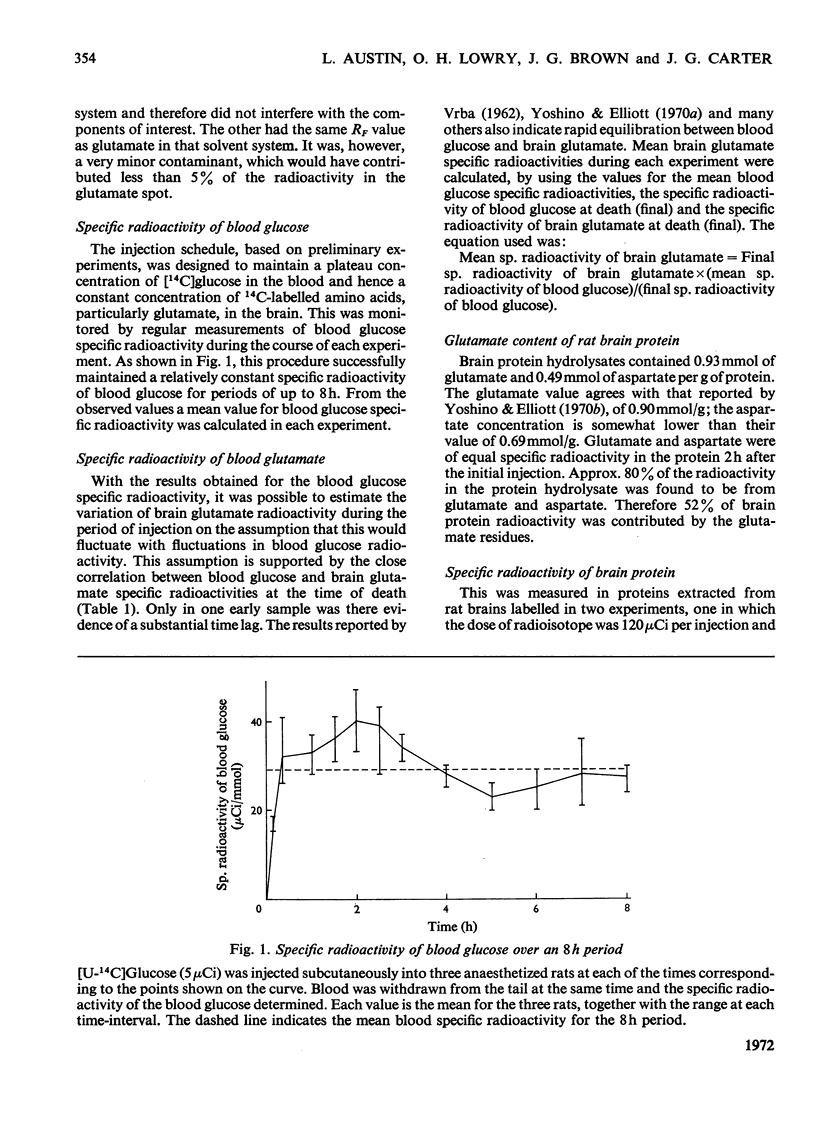
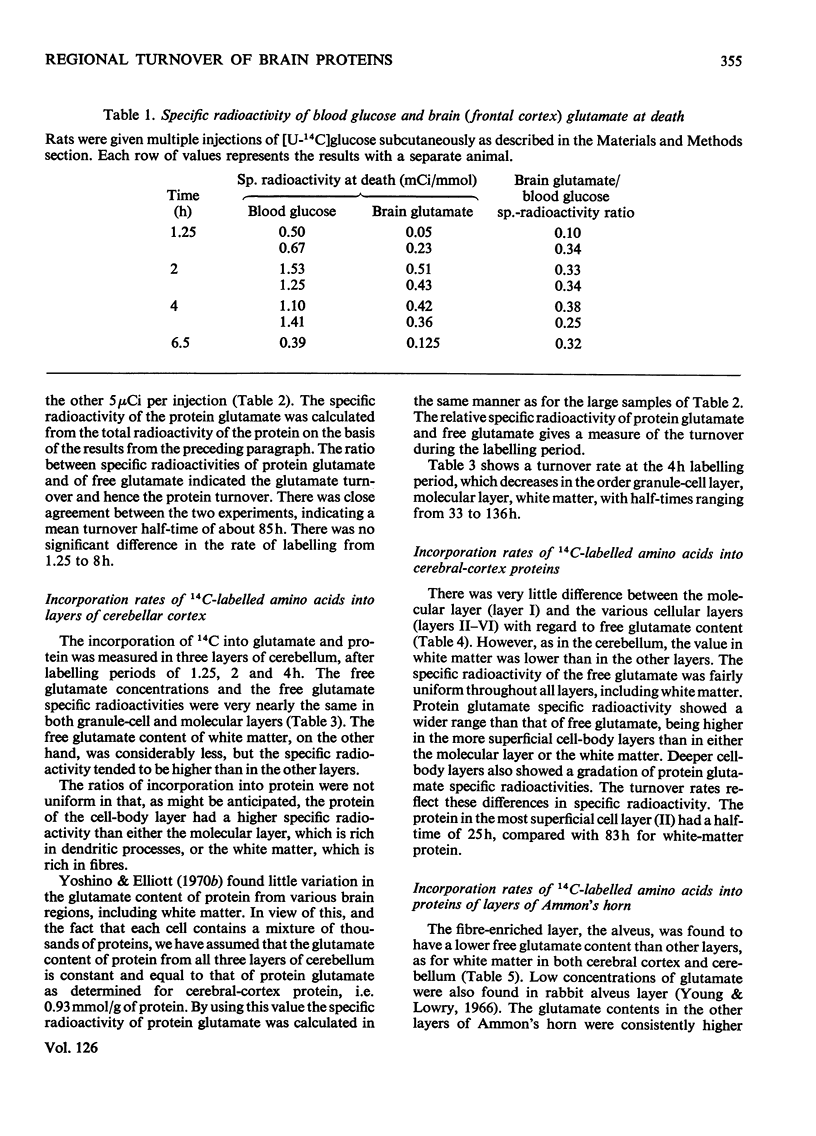
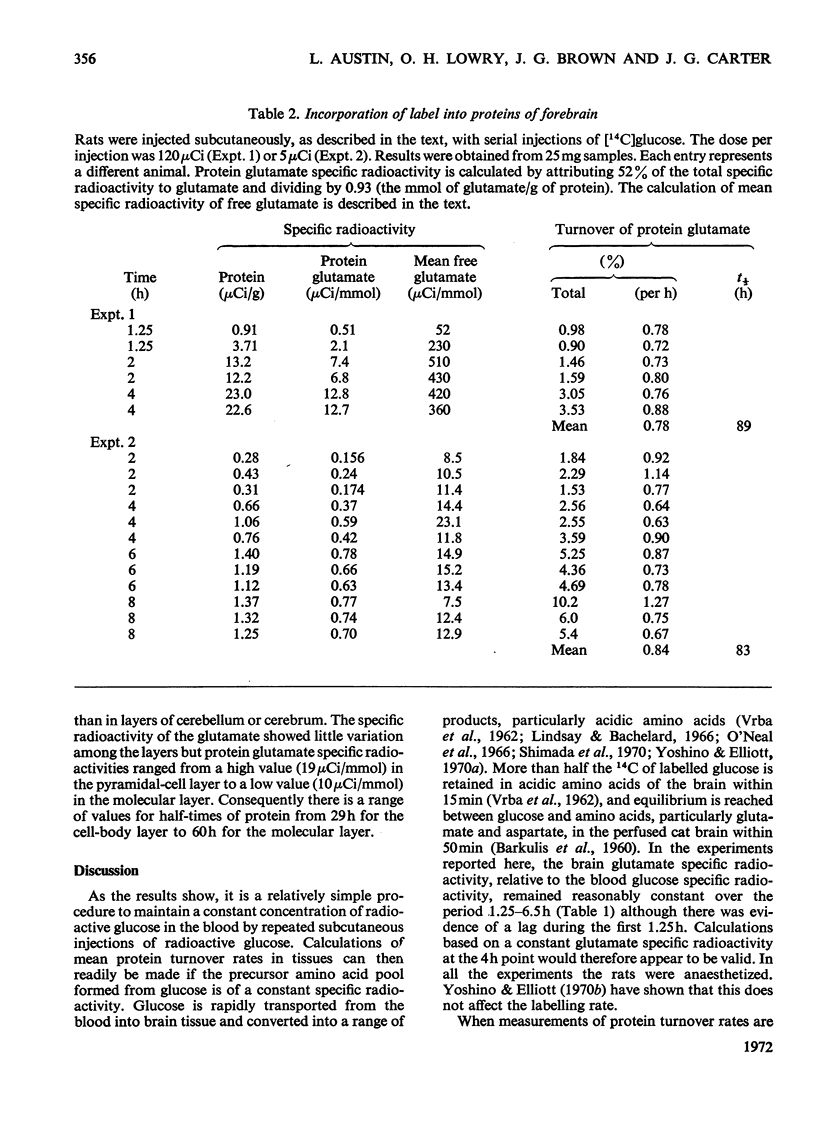
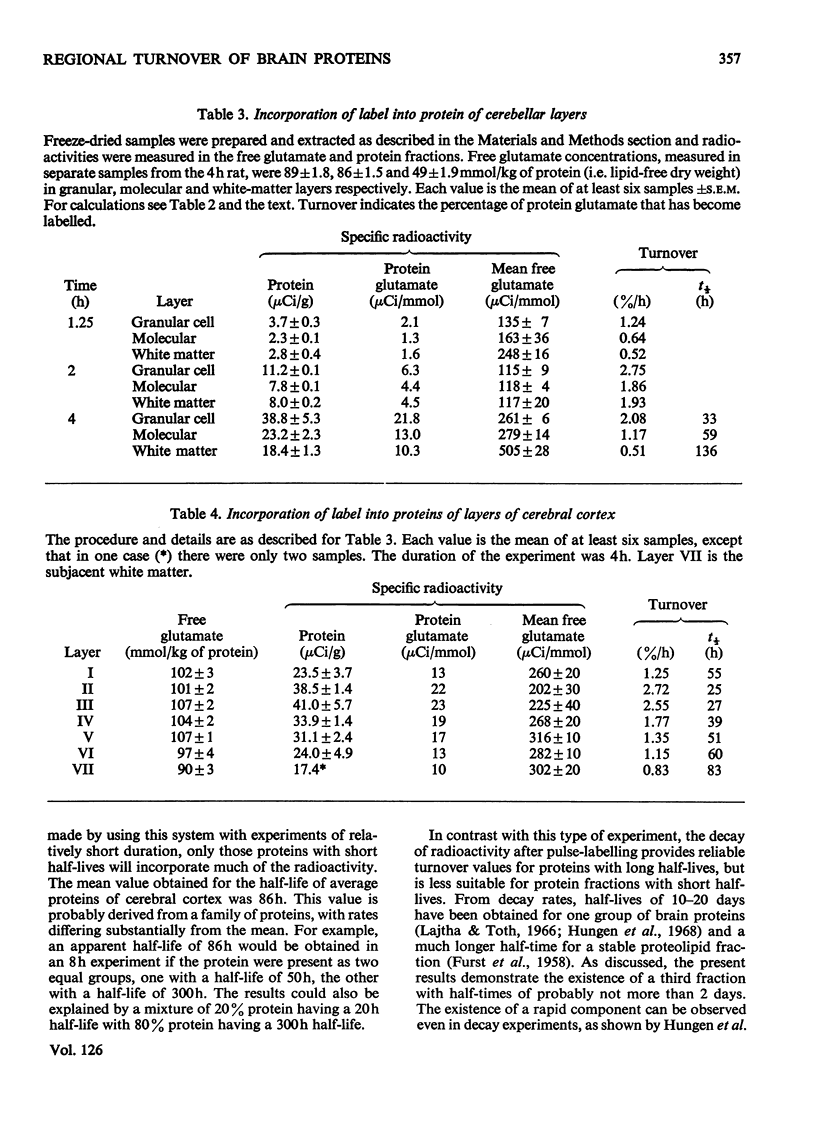
1. Rats were injected serially with [14C]glucose to obtain a constant specific radioactivity of brain amino acids. Measurements with this system for periods of up to 8h gave an apparent mean half-life for protein in whole brain of 85h (indicating the presence of a protein fraction with much more rapid turnover than this). 2. The half-lives of proteins in the granule-cell, molecular and white-matter layers of cerebellum were also determined. These had values of 33, 59 and 136h respectively. In addition, the incorporation into protein in six layers of the cerebral cortex, subjacent white matter and five layers of Ammon's horn was studied. All cell-body layers incorporated amino acids at about the same rate irrespective of location, and these rates were considerably higher than those for incorporation into proteins in areas rich in dendrites or fibre tracts. 3. A new method for measuring small amounts of glutamate with a cyclic enzyme system is presented.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKULIS S. S., GEIGER A., KAWAKITA Y., AGUILAR V. A study on the incorporation of 14C derived from glucose into the free amino acids of the brain cortex. J Neurochem. 1960 Jun;5:339–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomstrand C., Hamberger A. Protein turnover in cell-enriched fractions from rabbit brain. J Neurochem. 1969 Sep;16(9):1401–1407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray J. J., Austin L. Axoplasmic transport of 14C proteins at two rates in chicken sciatic nerve. Brain Res. 1969 Jan;12(1):230–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicero T. J., Moore B. W. Turnover of the brain specific protein, S-100. Science. 1970 Sep 25;169(3952):1333–1334. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3952.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURST S., LAJTHA A., WAELSCH H. Amino acid and protein metabolism of the brain. III. Incoporation of lysine into the proteins of various brain areas and their cellular fractions. J Neurochem. 1958;2(2-3):216–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming M. C., Lowry O. H. The measurement of free and N-acetylated aspartic acids in the nervous system. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):779–783. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGER A., HORVATH N., KAWAKITA Y. The incorporation of 14C derived from glucose into the proteins of the brain cortex, at rest and during activity. J Neurochem. 1960 Jun;5:311–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuditta A., Dettbarn W. D., Brzin M. Protein synthesis in the isolated giant axon of the squid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG E. SYNTHETIC MECHANISMS IN THE AXON. I. LOCAL AXONAL SYNTHESIS OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:343–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., KAPPHAHN J. I. The fluorometric measurement of pyridine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):1047–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H. The quantitative histochemistry of the brain; histological sampling. J Histochem Cytochem. 1953 Nov;1(6):420–428. doi: 10.1177/1.6.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lajtha A., Toth J. Instability of cerebral proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 3;23(3):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90544-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay J. R., Bachelard H. S. Incorporation of 14C from glucose into alpha-keto acids and amino acids in rat brain and liver in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Aug;15(8):1045–1052. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. S., Grafstein B. Fast and slow components in axonal transport of protein. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):494–508. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan I. G., Austin L. Synaptosomal protein synthesis in a cell-free system. J Neurochem. 1968 Jan;15(1):41–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. R., Schulz D. W., Passonneau J. V., Lowry O. H. Control of glycogen levels in brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Nov;15(11):1271–1279. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neal R. M., Koeppe R. E., Williams E. I. Utilization in vivo of glucose and volatile fatty acids by sheep brain for the synthesis of acidic amino acids. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):591–597. doi: 10.1042/bj1010591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., PALADE G. E. The fine structure of neurons. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):69–88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piha R. S., Cuénod M., Waelsch H. Metabolism of histones of brain and liver. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2397–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHTER D. Protein metabolism of the brain. Br Med J. 1959 May 16;1(5132):1255–1259. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5132.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada M., Iwata K., Inoue S., Otomo S., Kihara T. Distribution of radioactive carbon from [U]-14C-glucose in adult mice brains in vivo under normal conditions. Kaibogaku Zasshi. 1970 Jun 1;45(3):149–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiplady B., Rose S. P. Amino acid incorporation into protein in neuronal cell body and neuropil fractions in vitro. J Neurochem. 1971 Apr;18(4):549–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VRBA R., GAITONDE M. K., RICHTER D. The conversion of glucose carbon into protein in the brain and other organs of the rat. J Neurochem. 1962 Sep-Oct;9:465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb04199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VRBA R. Glucose metabolism in rat brain in vivo. Nature. 1962 Aug 18;195:663–665. doi: 10.1038/195663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hungen K., Mahler H. R., Moore W. J. Turnover of protein and ribonucleic acid in synaptic subcellular fractions from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1415–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINZLER R. J., MOLDAVE K., RAFELSON M. E., Jr, PEARSON H. E. Conversion of glucose to amino acids by brain and liver of the new-born mouse. J Biol Chem. 1952 Dec;199(2):485–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino Y., Elliott K. A. Effects of various conditions on the movement of carbon atoms derived from glucose into and out of protein in rat brain. Can J Biochem. 1970 Mar;48(3):236–243. doi: 10.1139/o70-043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino Y., Elliott K. A. Incorporation of carbon atoms from glucose into free amino acids in brain under normal and altered conditions. Can J Biochem. 1970 Mar;48(3):228–235. doi: 10.1139/o70-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. L., Lowry O. H. Quantitative methods for measuring the histochemical distribution of alanine, glutamate and glutamine in brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Sep;13(9):785–793. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb05873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


