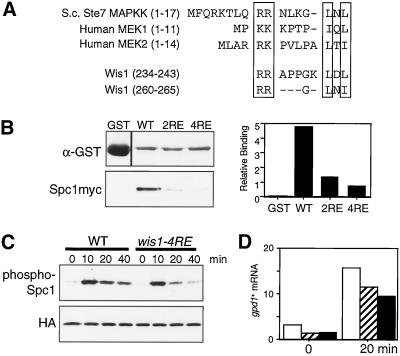
Figure 4.
MAPK docking site motifs in Wis1 MAPKK. (A) Residues 201–300 of Wis1 contain two sequences that resemble the MAPK-docking sites in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ste7 and human MEK1/MEK2 MAPKKs. The conserved two basic amino acid residues and L/I-X-L/I motifs are boxed. Either two or all four of the conserved arginine residues were substituted with glutamate to create the wis1-2RE or wis1-4RE alleles, respectively. (B) Glutathione-beads conjugated with bacterially produced GST, GST-Wis1, GST-Wis1-2RE, or GST-Wis1-4RE were mixed with S. pombe cell lysates from a spc1:myc strain (CA839). After extensive washes, proteins bound to the beads were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GST and anti-myc antibodies and quantified using the Storm System. (C) Defect in Spc1 activation in MAPK docking site mutant cells. wis1:GFP spc1:HA6H (CA1174) and wis1-4RE:GFP spc1:HA6H (CA1314) cells were grown to early-log phase at 30°C in YES medium and aliquots were harvested at the indicated time points after adding 0.3 M KCl to the cultures. Spc1HA6H was purified by Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid chromatography, followed by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-p38 MAPK and anti-HA antibodies. (D) The levels of the gpd1+ mRNA were determined by Northern blotting in the wis1:GFP spc1:HA6H (CA1174, open bars), wis1-4RE:GFP spc1:HA6H (CA1314, hatched bars), and wis1NLS:GFP spc1:HA6H (CA1225, filled bars) strains before and after a 20-min osmostress treatment by 0.3 M KCl. The quantified data are normalized using the leu1+ probe as control. Numbers are in arbitrary units.