Abstract
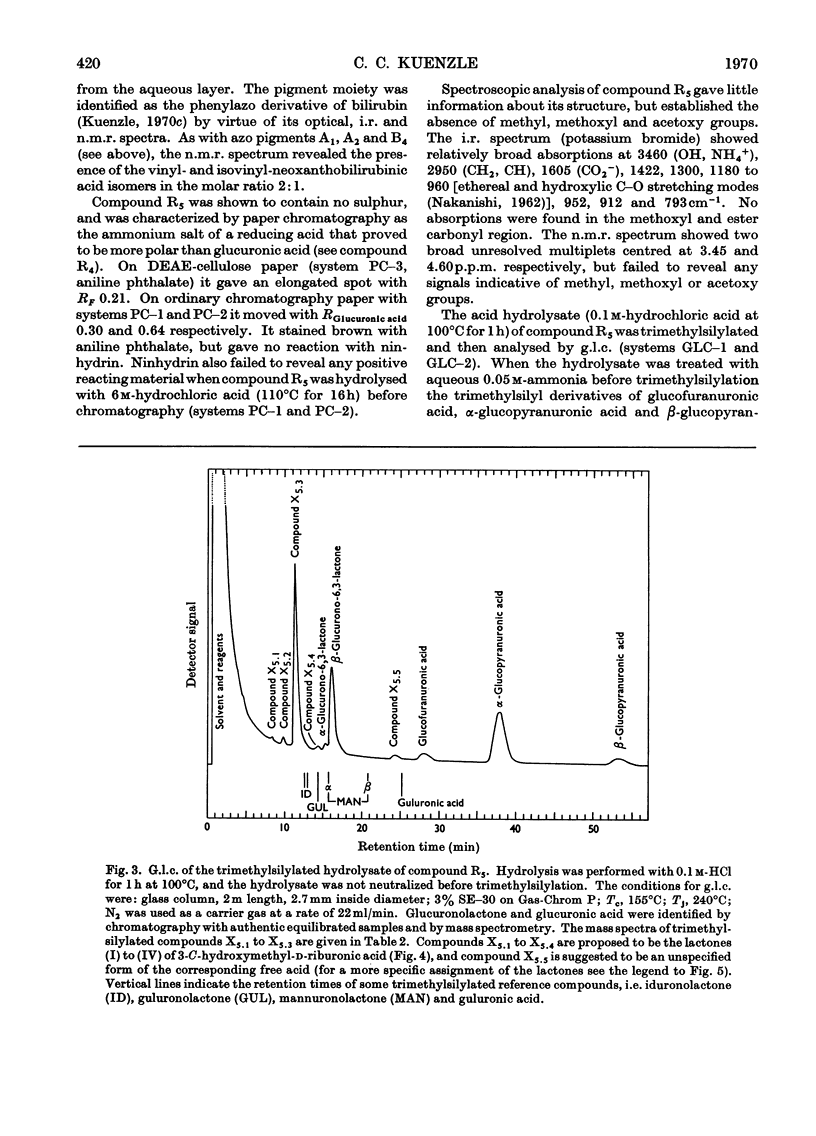
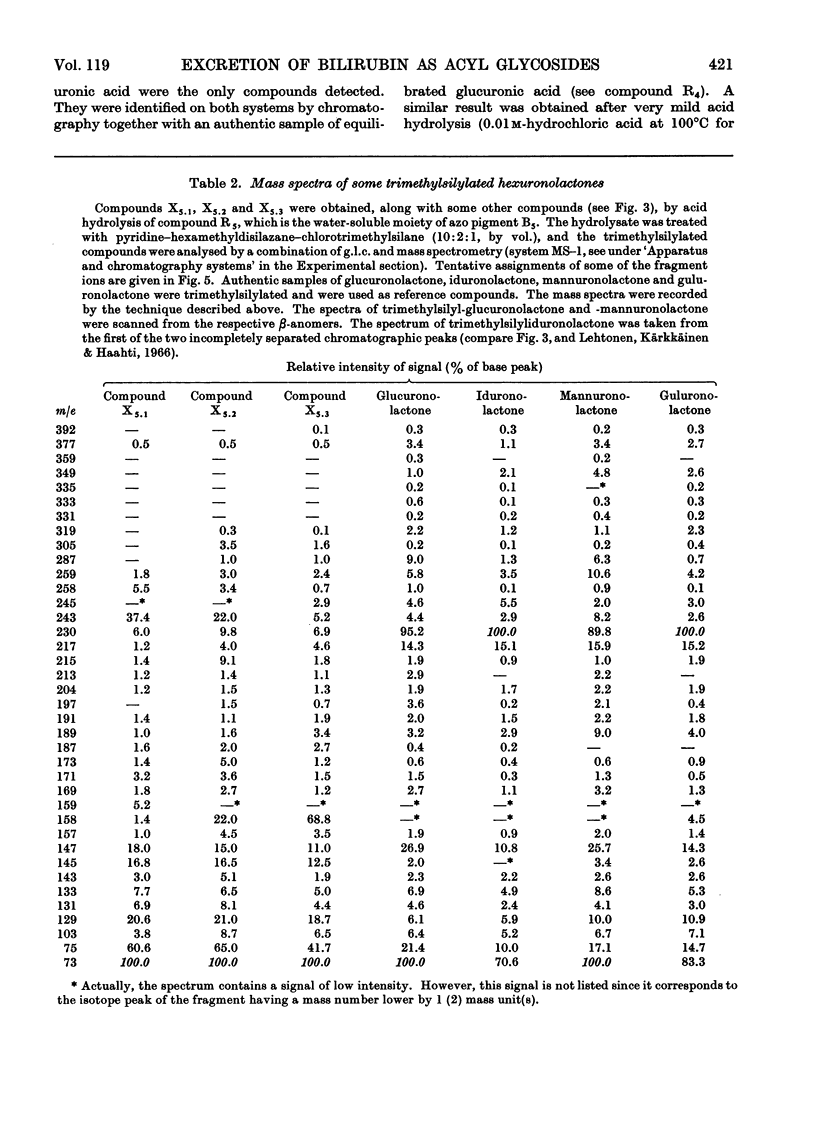
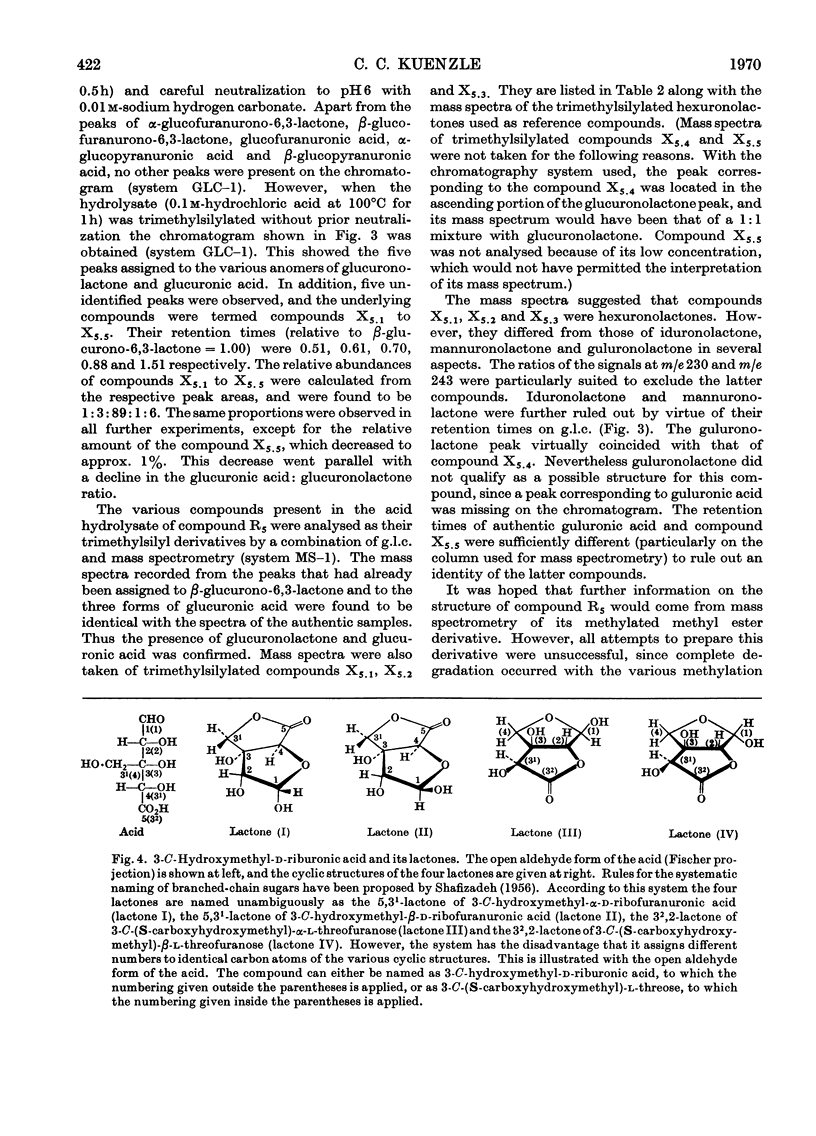
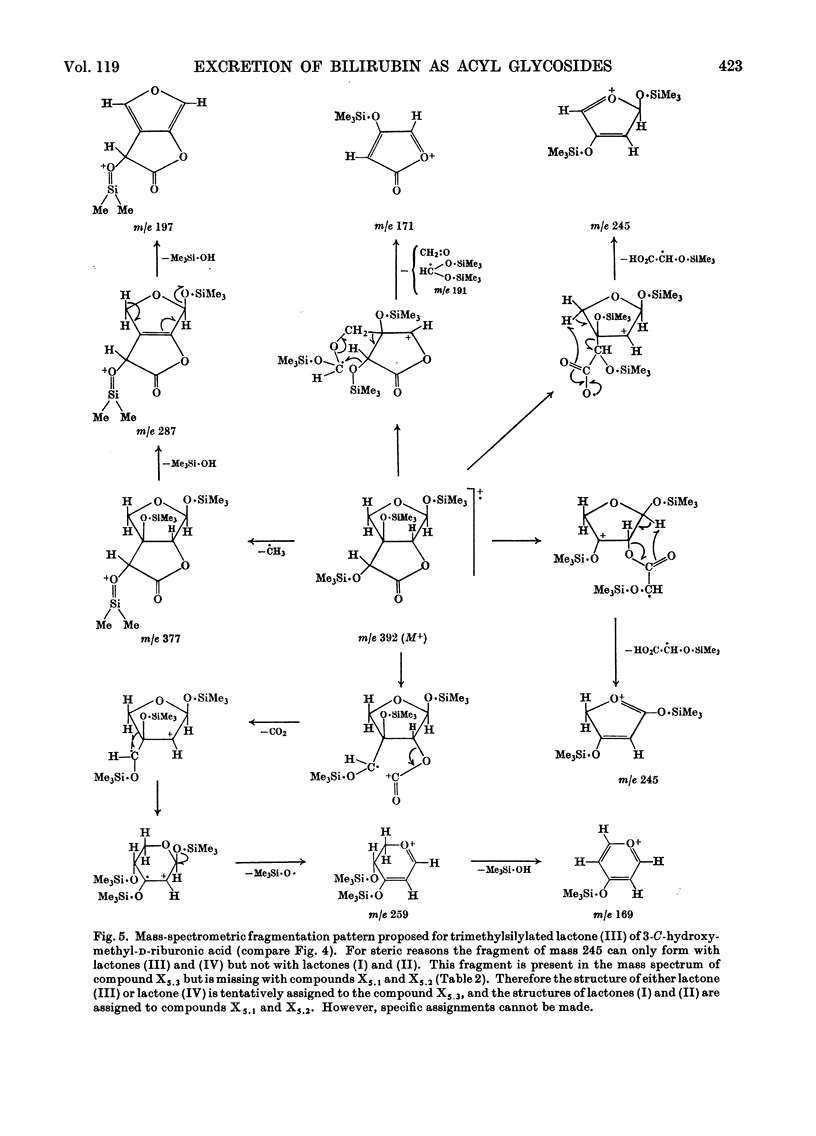
Structure elucidations have been performed on the bilirubin conjugates isolated from human hepatic bile as the phenylazo derivatives. The major bilirubin conjugates are excreted, not as was formerly thought in the form of glucuronides, but as the acyl glycosides of aldobiouronic acid, pseudoaldobiouronic acid and hexuronosylhexuronic acid. The isolated aldobiouronides are proposed to have the structures of an acyl 6-O-hexopyranosyluronic acid-hexopyranoside, an acyl 4-O-hexofuranosyluronic acid-d-glucopyranoside, and an acyl 4-O-β-d-glucofuranosyluronic acid-d-glucopyranoside respectively, with the acyl radicals being those of the phenylazo derivative of bilirubin. The pseudoaldobiouronide is suggested to be the acyl 4-O-α-d-glucofuranosyl-β-d -glucopyranosiduronic acid, with the acyl radical being that of the phenylazo derivative of vinylneoxanthobilirubinic acid. The hexuronosylhexuronide presumably is the acyl 4-O-(3-C-hydroxymethylribofuranosyluronic acid)-β-d-glucopyranosiduronic acid, with the acyl radical being that of the phenylazo derivative of bilirubin. The 3-C-hydroxymethylriburonic acid, isolated as one of the components of the hexuronosylhexuronide, is the first natural branched-chain hexuronic acid to be detected, and the first branched-chain sugar ever detected in humans.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BILLING B. H., COLE P. G., LATHE G. H. The excretion of bilirubin as a diglucuronide giving the direct van den Bergh reaction. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):774–784. doi: 10.1042/bj0650774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins D. L., Gitzelmann R., Lindenmann J., Semenza G. Immunochemical study of isolated human and rabbit intestinal sucrase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 13;160(3):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN W. H., GREEN S. Microanalysis of glucuronide glucuronic acid as applied to beta-glucuronidase and glucuronic acid studies. J Biol Chem. 1955 Aug;215(2):527–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY C. H., WATSON C. J. Studies of conjugated bilirubin. I. Comparison of conventional fractional determination with chromatographic and solvent partition methods for free and conjugated bilirubin. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Jul;60:1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY C. H., WATSON C. J. Studies of conjugated bilirubin. II. Problem of sulfates of bilirubin in vivo and in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Jul;60:17–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustine D. L., Kindel P. K. Biosynthesis of D-apiose in a cell-free system from Lemna minor L. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1382–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRASAKA Y., MATSUNAGA I., UMEMOTO K., SUKEGAWA M. [STUDIES ON THE ALPHA (1, 4) POLYSACCHARIDES OF GLUCURONIC ACID AND GLUCOSE. II. SYNTHESIS OF TRITYL-, TRITYLACETYLMALTOSE AND HEPTA-, HEXAACETYLMALTOSE]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1963 Oct;83:966–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirasaka Y., Matsunaga I. Studies on the alpha-(1,4)linked polysaccharides of D-glucuronic acid and D-glucose. VII. Synthesis of 4-O-(alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-glucuronic acid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1965 Feb;13(2):176–179. doi: 10.1248/cpb.13.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., McCARTHY E. A. Studies on bilirubin sulfate and other nonglucuronide conjugates of bilirubin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Apr;38(4):645–651. doi: 10.1172/JCI103842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO K., YOSHIDA K., TSUKAMOTO H. METABOLISM OF DRUGS. XLV. SYNTHESIS OF 2-NAPHTHYL BETA-D-GLUCOFURANOSIDURONIC ACID. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1964 Jun;12:664–669. doi: 10.1248/cpb.12.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO K., YOSHIDA K., TSUKAMOTO H. METABOLISM OF DRUGS. XLVI. BEHAVIOR OF 2-NAPHTHYL BETA-D-GLUCOFURANOSIDURONIC ACID TOWARD BETA-GLUCURONIDASE. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1964 Jun;12:670–674. doi: 10.1248/cpb.12.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochetkov N. K., Chizhov O. S. Mass spectrometry of carbohydrate derivatives. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1966;21:39–93. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60315-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolínská J., Semenza G. Studies on intestinal sucrase and on intestinal sugar transport. V. Isolation and properties of sucrase-isomaltase from rabbit small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):181–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C. Bilirubin conjugates of human bile. Isolation of phenylazo derivatives of bile bilirubin. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj1190387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C. Bilirubin conjugates of human bile. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance, infrared and optical spectra of model compounds. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(3):395–409. doi: 10.1042/bj1190395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzle C. C., Maier C., Rüttner J. R. The nature of four bilirubin fractions from serum and of three bilirubin fractions from bile. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Feb;67(2):294–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R., SCHMID R. Intestinal absorption of bile pigments. I. The enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1963 May;42:736–746. doi: 10.1172/JCI104766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R., SCHMID R. Intestinal absorption of bile pigments. II. Bilirubin absorption in man. N Engl J Med. 1963 Jul 25;269:178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196307252690402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD A. G., TUDBALL N., DODGSON K. S. Infrared studies on sulphate esters. III. O-Sulphate esters of alcohols, amino alcohols and hydroxylated amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 30;52:413–419. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen A., Kärkkäinen J., Haahti E. Gas-chromatographic characterization of the electrophoretically separated fractions of acid mucopolysaccharides. J Chromatogr. 1966 Sep;24(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)98120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noir B. A., Groszman R. J., De Walz A. T. Studies on bilirubin sulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 25;117(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Suzuki N., Suzuki S. Biosynthesis of branched chain deoxysugars. IV. Isolation of cytidine diphosphate 6-deoxy-3-C-methyl-2-O-methyl-4-O-(O-methyl-glycolyl)-L-aldohexopyranoside from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6353–6360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda S., Suzuki N., Suzuki S. Isolation and structure of cytidine diphosphate 6-deoxy-3-C-methyl-2-O-methyl-L-aldohexopyranoside (cytidine diphosphate vinelose) from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):958–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raunhardt O., Schmidt H. W., Neukom H. Gas-chromatographische Untersuchungen an Uronsäuren und Uronsäurederivaten. Helv Chim Acta. 1967 Jul 10;50(5):1267–1274. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19670500508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID R. The identification of direct-reacting bilirubin as bilirubin glucuronide. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENFIELD L. J., BOLLMAN J. L., HOFFMAN H. N., 2nd Sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of bilirubin in experimental liver injury. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jan;41:133–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI104455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAFIZADEH F. Branched-chain sugars of natural occurrence. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1956;48(11):263–283. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G., Curtius C. H., Kolínská J., Müller M. Studies on intestinal sucrase and intestinal sugar transport. VI. Liberation of alpha-glucose by sucrase and isomaltase from the glycone moiety of the substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):196–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALAFANT E. Properties and composition of the bile pigment giving a direct diazo reaction. Nature. 1956 Aug 11;178(4528):312–312. doi: 10.1038/178312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Inducible polysaccharide depolymerases of Bacillus palustris. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:3–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEGAS F. R. Chromatographic behavior on ion-exchange paper of bilirubin conjugated with sulfate and glucuronide. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jun;5:465–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER A. P., SCHALM L. EVIDENCE AGAINST "BILIRUBIN SULPHATE". Acta Med Scand. 1965 Apr;177:519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHISTLER R. L., BEMILLER J. N. Alkaline degradation of polysaccharides. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1958;13:289–329. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


