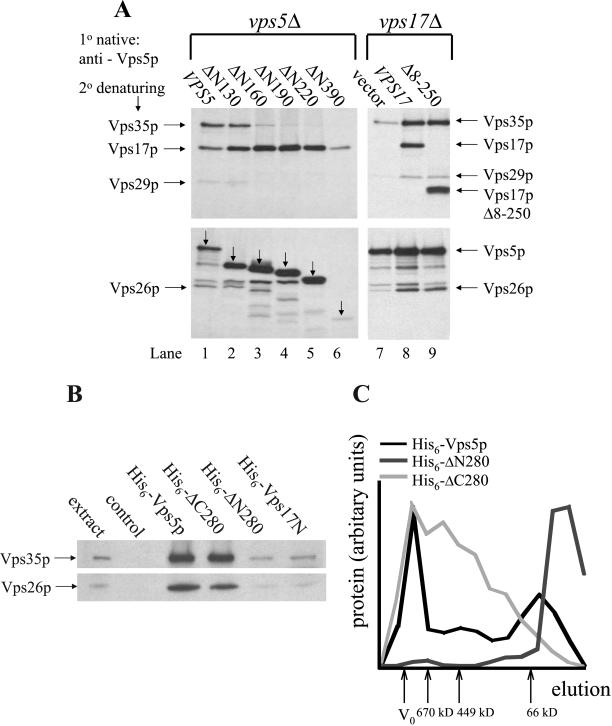
Figure 6.
(A) Truncation of Vps5p N-terminal half ablates the interaction with Vps35p, Vps29p, and Vps26p. vps5Δ or vps17Δ cells expressing the respective truncations from CEN plasmids were pulse labeled for 20 min with [35S]methionine and chased for 40 min with excess unlabeled methionine. After lysis, Vps5p was immunoprecipitated under native conditions. Vps35p, Vps17p, Vps29p, Vps26p, and also Vps5p (indicated with the downward pointing arrows) were subsequently immunoprecipitated under denaturing conditions and then subjected to SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal half of Vps5p seems to be necessary for interactions with other retromer components, whereas binding of Vps17p (full length or truncated) to Vps5p seems to facilitate the interactions with Vps35p, Vps29p, and Vps26p. (B) Recombinant His6-tagged Vps5p can bind to Vps35p and Vps26p. Bacterially expressed His6-fusion proteins purified on Ni2+-agarose were incubated with a yeast lysate. After several washes of the Ni2+-agarose, the bound proteins were eluted with 250 mM imidazole, precipitated, and then subjected to SDS-PAGE. Vps35p and Vps26p were detected by Western blotting. The N-terminal half of Vps5p is sufficient for interactions with Vps35p and Vps26p. (C) Self-assembly activity is mediated by the N-terminal half of Vps5p. Bacterially expressed His6-fusion proteins purified on Ni2+-agarose were dialyzed against cytosol buffer and then size fractionated on a Sephacryl S300 column. Fractions were analyzed for fusion protein by SDS-PAGE. The gels were scanned and the amount of fusion protein present in each fraction quantitated using NIH Image software.