Abstract
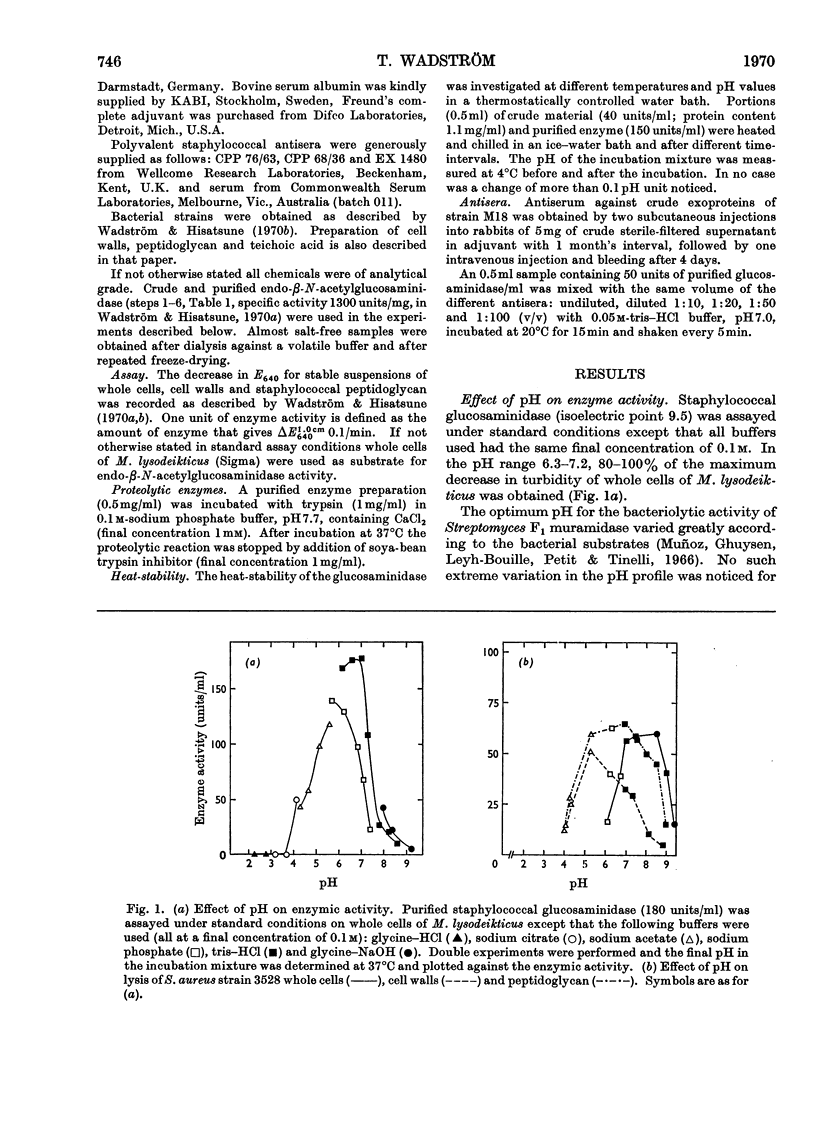
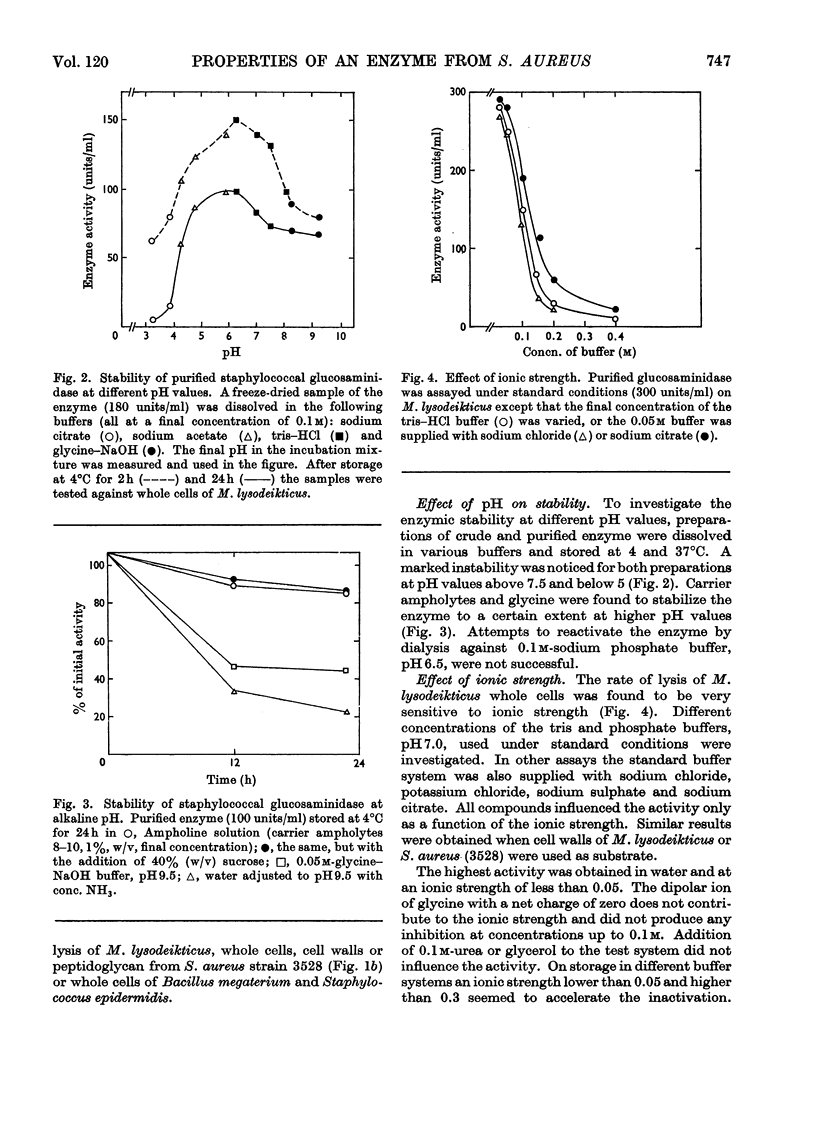
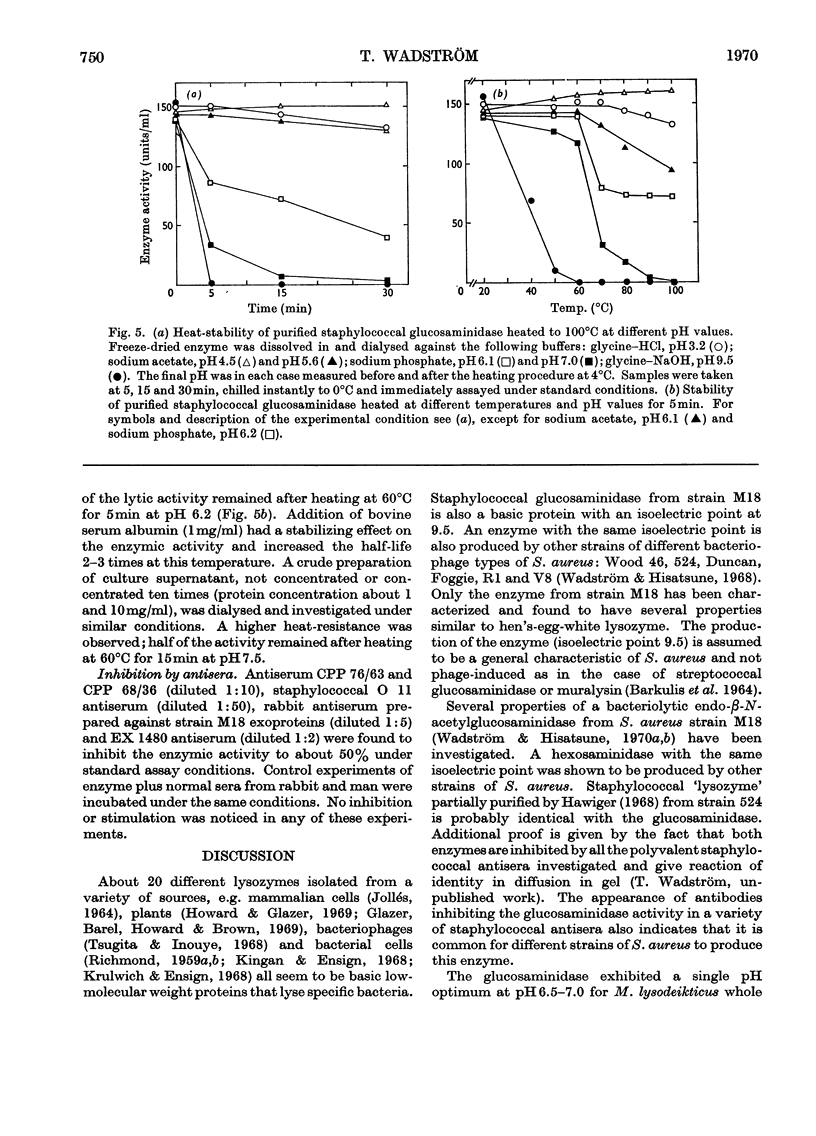
An extracellular bacteriolytic endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase has been purified and its specificity of action has been investigated (Wadström & Hisatsune, 1970a,b). Some enzymic properties, such as optimum pH for enzyme activity on whole cells and cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus and Staphylococcus aureus and optimum pH for stability, have been studied. The activity was maximum in 0.05m-tris–hydrochloric acid buffer, pH7.0. A higher ionic strength inhibited cell-wall hydrolysis. Since the crude and purified enzymes were found to be unstable on storage, the stabilizing and inhibiting effects of several compounds were investigated. Several heavy metal ions inactivated the enzyme at very low concentrations. Thiol compounds stabilized and thiol-reacting compounds partly inhibited the activity. Crude and purified glucosaminidase was found to be heat-stable at acidic pH and unstable at alkaline pH as previously found for several lysozymes (endo-β-N-acetylmuramidases). Other properties of the staphylococcal enzyme and hen's-egg-white lysozyme have been compared, since the modes of action of the two are quite similar (Wadström & Hisatsune, 1970b).
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARKULIS S. S., SMITH C., BOLTRALIK J. J., HEYMANN H. STRUCTURE OF STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. IV. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STREPTOCOCCAL PHAGE MURALYSIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke M. E., Pattee P. A. Purification and characterization of a staphylolytic enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):860–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.860-865.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPUTO A. Interaction of pepsin with lysozyme. Experientia. 1955 Oct 15;11(10):400–401. doi: 10.1007/BF02158506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. C., Neuberger A., Wilson B. M. The dependence of lysozyme activity on pH and ionic strength. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;178(2):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensign J. C., Wolfe R. S. Characterization of a small proteolytic enzyme which lyses bacterial cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):524–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.524-534.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEENEY R. E., MACDONNELL L. R., DUCAY E. D. Irreversible inactivation of lysozyme by copper. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Mar;61(1):72–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHUYSEN J. M., STROMINGER J. L. STRUCTURE OF THE CELL WALL OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, STRAIN COPENHAGEN. I. PREPARATION OF FRAGMENTS BY ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1110–1119. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N., Barel A. O., Howard J. B., Brown D. M. Isolation and characterization of fig lysozyme. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3583–3589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASH J. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STAPHYLOLYTIC ENZYMES FROM CHALAROPSIS SP. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Sep;102:379–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J. Purification and properties of lysozyme produced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.376-384.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Glazer A. N. Papaya lysozyme. Terminal sequences and enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1399–1409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingan S. L., Ensign J. C. Isolation and characterization of three autolytic enzymes associated with sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):629–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.629-638.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Ensign J. C. Activity of an autolytic N-acetylmuramidase during sphere-rod morphogenesis in Arthrobacter crystallopoietes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):857–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.857-859.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARRY R. M., Jr, CHANDAN R. C., SHAHANI K. M. A RAPID AND SENSITIVE ASSAY OF MURAMIDASE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jun;119:384–386. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J. F., Munoz E., Ghuysen J. M. Peptide cross-links in bacterial cell wall peptidoglycans studied with specific endopeptidases from Streptomyces albus G. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2764–2776. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryme I. F., Joner P. E., Jensen H. B. The isolation of an inhibitor of T-even phage lysozyme from E. coli B cells. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jul;4(1):50–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. The properties of lysozyme and its action on microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Jun;21(2):82–100. doi: 10.1128/br.21.2.82-100.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOLELIS A. N., HARTSELL S. E. Factors affecting the lytic activity of lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1952 May;63(5):665–674. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.5.665-674.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Ghuysen J. M. Mechanisms of enzymatic bacteriaolysis. Cell walls of bacteri are solubilized by action of either specific carbohydrases or specific peptidases. Science. 1967 Apr 14;156(3772):213–221. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3772.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Mechanism of autolysis of isolated cell walls of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):837–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.837-847.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Inouye M. Complete primary structure of phage lysozyme from Escherichia coli T4. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Hisatsune K. Bacteriolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. Specificity of ction of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):735–744. doi: 10.1042/bj1200735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B., Perkins H. R. The purification and properties of two staphylolytic enzymes from Streptomyces griseus. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):69–76. doi: 10.1042/bj1060069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZYSKIND J. W., PATTEE P. A., LACHE M. STAPHYLOLYTIC SUBSTANCE FROM A SPECIES OF PSEUDOMONAS. Science. 1965 Mar 19;147(3664):1458–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3664.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


