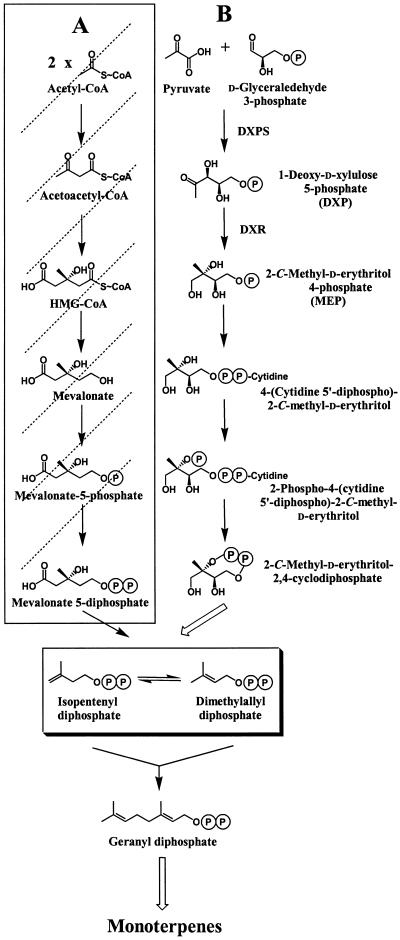
Figure 1.
Monoterpene biosynthesis in peppermint oil gland secretory cells. In plants, two independent pathways are used in the formation of the central precursors of isoprenoids, IPP, and DMAPP: the cytosolic mevalonate pathway (A) and the plastidial mevalonate-independent pathway (B; Lange et al., 2000b). Further reactions include the conversion of IPP to DMAPP, catalyzed by IPP isomerase (Ogura, 1999), followed by sequential condensation reactions catalyzed by prenyltransferases (Ogura, 1999). These prenyl diphosphates (e.g. geranyl diphosphates) undergo cyclizations and subsequent secondary transformation (largely redox) reactions leading to diverse isoprenoid end products (McGarvey and Croteau, 1995). In peppermint secretory cells, the mevalonate pathway is blocked as indicated by dotted lines (McCaskill and Croteau, 1995), making these cells an excellent in vivo system for studying herbicide effects on the mevalonate-independent pathway.