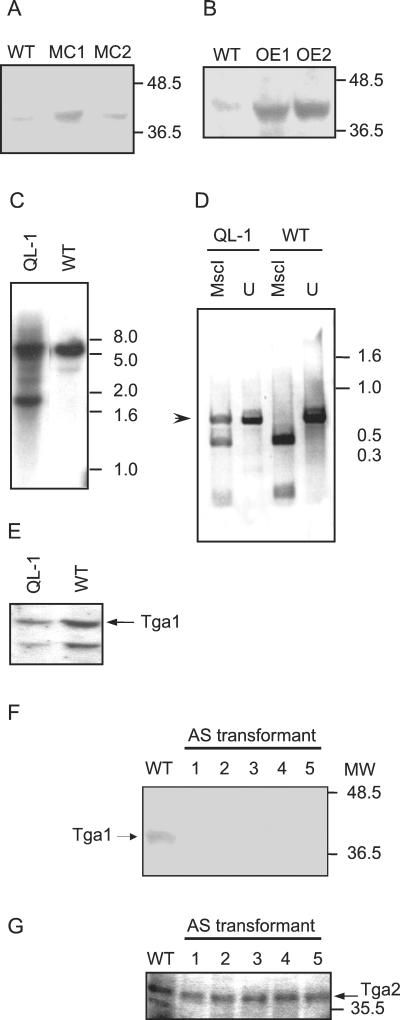
FIG. 3.
Expression of Tga1 in wild-type and transgenic Trichoderma strains. (A and B) Western blots of membrane fractions from the indicated strains probed with antibody to Gna1. WT, wild type. (A) Lines MC1 and MC2, carrying multiple copies of tga1. (B) Lines OE1 and OE2, expressing tga1 from the prb1 promoter. (C) Southern analysis of wild-type and transgenic strains carrying a mutant allele of tga1. Genomic DNAs from the two strains were digested with EcoRI, and the blot was probed with a 1.2-kb EcoRV genomic fragment. Thepositions of molecular size markers are indicated at the right in kilobases. (D) Detection of expression of the mutant tga1 allele. RNA was extracted and used as a template for RT and PCR amplification as described in Materials and Methods. The products were digested to completion with MscI or left undigested (U). The arrowhead indicates the expected cDNA product of the mutant gene, which cannot be digested with MscI. DNA molecular size markers are indicated at the right in kilobases. (E) Immunoblot analysis of transformants carrying the mutant tga1 allele. Membrane protein fractions from wild-type and transformant strains were analyzed as described in panel A. The arrow indicates the signal corresponding to Tga1. (F and G) Immunoblot analyses of transformants expressing tga1 in the antisense (AS) form. Shown are Western blots of membrane fractions from the indicated transformants probed with antibody to Gna1 (F) or Gna2 (G) of N. crassa. MW, molecular weight, in thousands.