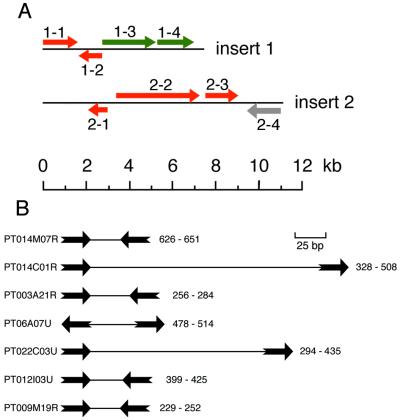
FIG. 8.
Gene density. (A) ORF distribution of two complete library inserts. Colors: red, ORFs validated by significant BLASTX matches; green, ORFs validated by homology-dependent gene silencing; gray, unvalidated potential ORF. 1-1, aminopeptidase (best score, 140); 1-2, pseudouridine synthase (best score, 112); 1-3, ND2 gene required for regulated exocytosis; 1-4, novel essential gene; 2-1, translation initiation factor EIF-2B subunit (best score, 102); 2-2, DNA repair protein RAD5 homolog (best score, 124) with a SNF2 family helicase domain; 2-3, slime mold interaptin homolog (score, 73); 2-4 potential ORF. (B) Intergenic regions separating ORFs for the seven GSS sequences which contain two putative ORFs, as revealed by BLASTX similarity searches. The sequence identification is given to the left of the map, and the first and last nucleotides of the intergenic region are shown to the right of the map. ORFs are pictured as thick arrows, and the intergenic regions are pictured as thin lines. The ORFs are as follows: PT014M07R, TMP4a secretory granule protein and PRP8 splicing factor; PT014C01R, homolog of unknown Drosophila gene and RAC protein kinase; PT003A21R, unknown kinase and MEK kinase; PT006A07U, hypothetical protein and PRP19 splicing factor; PT022C03U, ribosomal protein L33 and YPT1-like GTP-binding protein; PT012I03U, ribosomal protein L36 and CTP phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase; and PT009 M19R, small GTP-binding protein and ring zinc-finger protein.