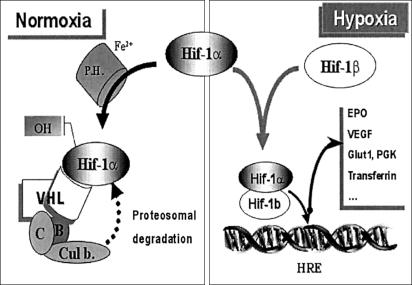
Figure 1.
Hypoxia-sensing pathway. The hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) is a master regulator of hypoxia. In normoxia, HIF-1α is hydroxylated by proline hydroxylase; pVHL binds to the hydroxylated form of HIF-1α and serves as the recognition component of an E3-ubiquitin ligase complex that comprises elongins B (B) and C (C), Cullin 2, and ring-box 1; this includes a proteosomal degradation of HIF-1α. In hypoxia, HIF-1α accumulates and forms a heterodimer with HIF-1β that will bind to hypoxia-responsive elements (HRE) and leads to an increased synthesis of the related hypoxia-responsive genes, such as EPO, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), glucose transporter 1 (Glut1), phospho-glycerate kinase (PGK), transferrin and its receptor, and other genes.