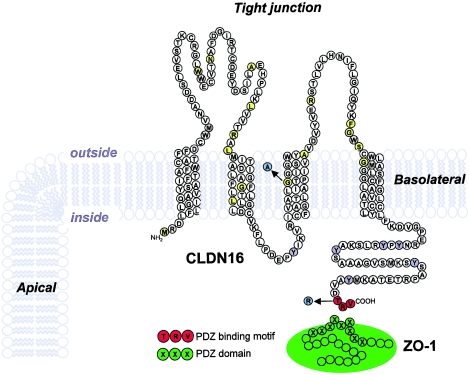
Figure 2.
Predicted topology of CLDN16 and location of the different mutations reported. Shown is the amino acid sequence from the second translation-initiation site, which is used in vivo (Ohba et al. 2000; Weber et al. 2001a, 2001b). Mutated amino acids thus far reported in the literature that are associated with classical FHHNC are shown (Simon et al. 1999; Weber et al. 2000; Weber et al. 2001b) (yellow), with the G128A mutation characterized in this study highlighted (blue). The C-terminal PDZ binding motif (red) and the novel T233R mutation encountered in the patients of families A and B (blue) are also shown. Tyrosine residues in the C-terminal cytosolic domain of CLDN16 that may be part of endocytosis and/or lysosomal sorting signals are indicated (gray).