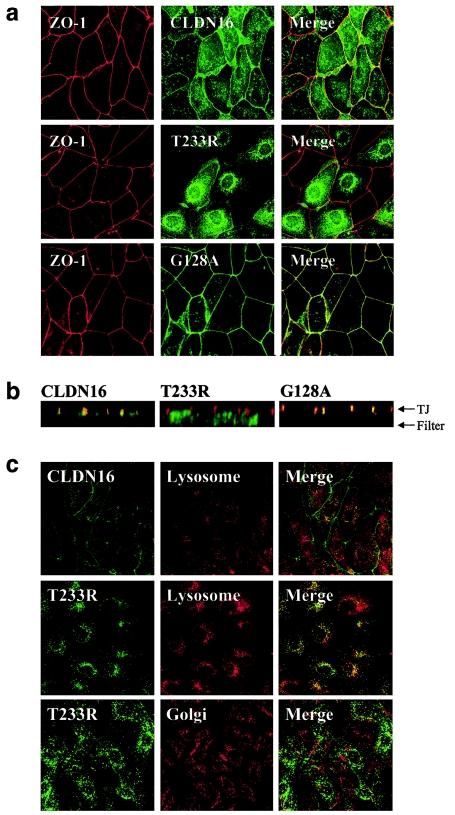
Figure 4.
Subcellular localization of wild-type and mutant CLDN16. a, Colocalization of CLDN16 and ZO-1 is abolished by the T233R mutation. MDCK cells stably expressing wild-type (CLDN16) or mutant (T233R or G128A) CLDN16 grown as polarized cell monolayers on polycarbonate filters were stained for ZO-1 (red) and CLDN16 (green), and confocal images corresponding to horizontal sections at the height of TJ were acquired. The merged image shows regions where CLDN16 and ZO-1 colocalize (yellow). b, TJ localization of CLDN16 is abolished by the T233R mutation. Vertical confocal sections along the apico-basal axis of the cell monolayers expressing wild-type (CLDN16) or mutant (T233R or G128A) CLDN16 labeled for CLDN16 (green) or ZO-1 (red). The positions of the filter supporting the cells and the TJ are indicated. c, T233R localized to lysosomes. MDCK cells transfected with wild-type (CLDN16) or mutant (T233R) CLDN16 were stained to visualize lysosomes (anti–lamp-2) or the Golgi complex (anti-GM130) (red) and CLDN16 (green), and confocal images were acquired. The T223R mutant shows extensive localization to lyososmes (merged image; yellow), but not the Golgi complex.