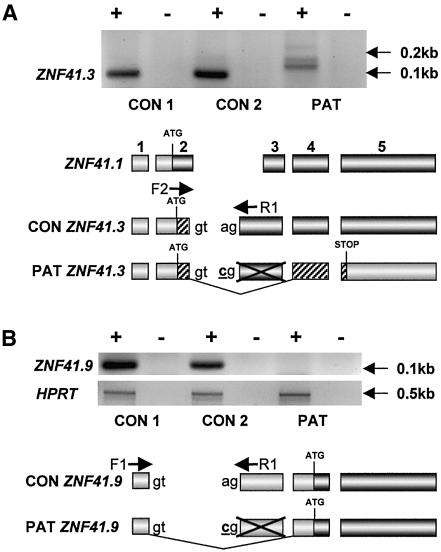
Figure 5.
A, RT-PCR for ZNF41.3 in male control (CON 1), female control (CON 2), and patient (PAT) lymphoblastoid cell lines. The schematic diagram below the cell lines (not to scale) indicates the exonic structure of both normal and predicted aberrant ZNF41.3 transcripts, with respect to the predominant transcript variant ZNF41.1, and the respective locations of primers F2 and R1 (specific for variants 41.3 and 41.6) used for amplification. Shaded regions indicate predicted coding sequence; patterns differentiate between reading frames. The adenine→cytidine intronic splice-site mutation in the patient is underlined and indicated in bold typeface. B, RT-PCR for the novel transcript variant ZNF41.9 in the same samples. As in section A, the schematic diagram indicates the intronic mutation, the structure of ZNF41.9 relative to the predominant transcript ZNF41.1, the location of primers F1 and R1 used for amplification, and the predicted coding sequences of the resulting transcript variants. Amplification of HPRT served as a control. A plus sign (+) indicates with reverse transcriptase; a minus sign (−) indicates mock reaction.