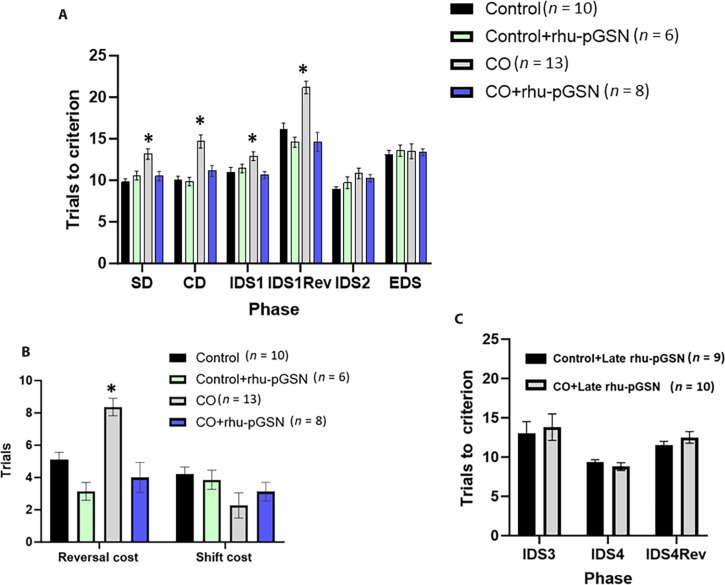
Fig. 6. Attentional set shift scores for control and CO-exposed mice.
(A) Trials to criterion for progressive tasks. Where indicated, rhu-pGSN injection occurred immediately after CO exposure and control mice injected at the same time. The CO group demonstrated differences on each of the first four phases, the smallest value F(3,33) = 4.09, P < 0.01 (ANOVA). The CO mice significantly differed from control mice on each of these phases, P < 0.05 (*). The trials to criterion to complete each phase was significant, F(5,165) = 53.55, P < 0.001 (RM-ANOVA) as a phase × exposure interaction, F(5,165) = 2.91, P < 0.015, and phase × treatment interaction, F(5,165) = 5.71, P < 0.001. The main effects of CO, F(1,33) = 22.89, P < 0.001, rhu-pGSN treatment, F(1,33) = 15.53, P < 0.001, and the interaction, F(1,33) = 19.10, P < 0.001, were significant. (B) Reversal and extradimensional shift cost scores. No significant differences were detected on the extradimensional shift cost, but CO-exposed mice were significantly less likely to demonstrate an attentional set formation as confirmed by the χ2 statistic. Values are mean ± SD, * indicates P < 0.05 versus control. (C) Effect of late rhu-pGSN administration. After tasks were performed as in (B), mice were injected with rhu-pGSN so that during the third week, repetitive IDS testing (IDS 3 and 4) and reversal tasks were assessed. No significant differences between CO-exposed and control mice were found.