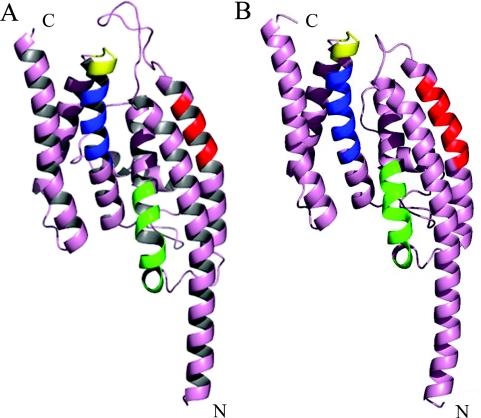
Figure 2.
Homology-based model of the S.pombe Translin monomer. (A) The S.pombe sequence was folded using the human Translin crystal structure (1J1J) as its template, by the 3D-JIGSAW comparative modeling server. Putative functional domains are identified by colored ribbons: red, RNA-binding domain; green, DNA/RNA-binding domain, blue, nuclear export signal; yellow, GTP binding site. (B) Visualization of one monomer of the human Translin structure (1J1J). The color coding is the same as that of (A). As denoted in Figure 1, the positions of the human functional domains are predicted to be as follows: RNA-binding domain: amino acids 56–64; RNA- and DNA-binding domain: amino acids 86–97; nuclear export signal: amino acids 147–157; GTP binding site: amino acids 159–163.