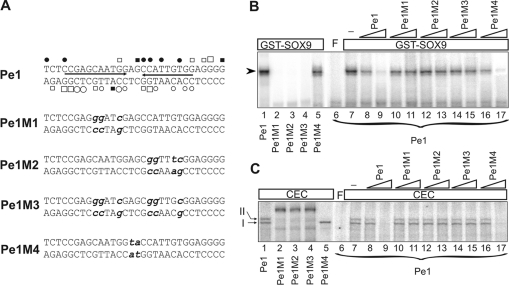
Figure 7. Mutational analysis of Pe1 by EMSA.
(A) Nucleotide sequences of the wild-type and mutant versions of Pe1. The inverted repeats (arrows) harbouring the paired Sox motifs as well as protections and hyperreactivities are indicated as in Figure 5. Point mutations presented in bold lower case letters were introduced at nucleotides, which showed in vivo occupancy at the Sox motifs or in the spacer region. (B) Interaction of the wild-type (lane 1) and mutant versions (lanes 2–5) of radiolabelled Pe1 with 2.0 μg of purified GST–SOX9. Binding of radiolabelled Pe1 to GST–SOX9 was competed by 50- and 500-fold molar excess of unlabelled normal and mutant Pe1 as indicated on the top (lanes 8–17). (C) EMSA was performed to compare the CEC nucleoprotein complexes formed on the wild-type and mutant Pe1 elements (lanes 1–5). Formation of CEC nucleoprotein complexes was competed with 50- and 500-fold molar excess of unlabelled Pe1 and its mutant versions as indicated on the top (lanes 8–17). No competitor was added to lane 7. F, free probe.