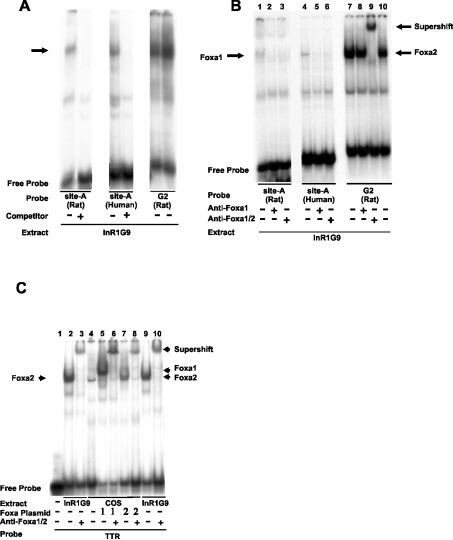
Figure 7. The novel Foxa site A in both the rat and human glucagon promoters binds preferentially to Foxa1 in nuclear extracts from a pancreatic islet α-cell line as indicated by the EMSA.
(A) Nuclear extracts from InR1G9 cells were probed with labelled oligonucleotides containing the Foxa site A of the rat glucagon promoter [site A (rat)], the Foxa site A of the human glucagon promoter [site A (human)] or, as a control, the G2 element of the rat glucagon promoter [G2 (rat)]. Where indicated, a 200-fold molar excess of unlabelled oligonucleotide (the same as probe) was added as a specific competitor. The band corresponding to specific binding is indicated by an arrow. (B) The Foxa site A-binding protein is recognized by a specific anti-Foxa1 antibody. Nuclear extracts from InR1G9 cells were incubated with labelled Foxa site A of the rat glucagon promoter [site A (rat)], Foxa site A of the human glucagon promoter [site A (human)] or, as a control, G2 of the rat glucagon promoter [G2 (rat)]. Preimmune IgG (2 μg) or antibodies recognizing specifically Foxa1 (anti-Foxa1) (0.5 μg) or antibodies recognizing Foxa1 and Foxa2 (anti-Foxa1/2) (2 μg) were added to the binding reaction as indicated. Note that the specific anti-Foxa1 antibody recognizes nuclear protein binding to the Foxa site A (both rat and human) but not nuclear protein binding to rat G2 (containing the Foxa site C). This shows the specificity of the anti-Foxa1 antibody and, at the same time, demonstrates that distinct nuclear proteins bind to the Foxa site A (Foxa1) and Foxa site C in G2 (Foxa2). (C) Binding specificity of the anti-Foxa1/2 antibody. Whole cell lysates from COS-1 cells transfected with expression vectors encoding Foxa1, Foxa2 or the empty vector were incubated with a labelled oligonucleotide (TTR) that contains a high-affinity Foxa-binding site from the mouse TTR gene promoter, which can be bound by each of the three major Foxa isoforms 1–3 [10,35]. Nuclear extracts of InR1G9 cells were included as controls. The anti-Foxa1/2 antibody was added to the binding reaction as indicated. Note that the complex formed by labelled TTR with COS-expressed Foxa1 as well as the complex formed by labelled TTR with COS-expressed Foxa2 is abolished and supershifted by the anti-Foxa1/2 antibody, indicating that this antibody (named anti-Foxa2 antibody by the manufacturer) recognizes both Foxa1 and Foxa2 under the conditions used.