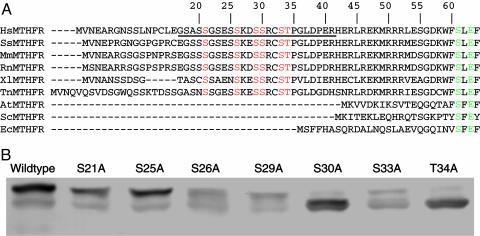
Fig. 5.
Mutational analysis of conserved serine and threonine residues in the N-terminal extension of human MTHFR. (A) Alignment of vertebrate sequences of the N-terminal extension of MTHFR. Abbreviations are as follows, with GenBank accession nos. in parentheses: HsMTHFR, Homo sapiens MTHFR (U09806); SsMTHFR, Sus scrofa MTHFR (AW619446); MmMTHFR, Mus musculus MTHFR (BC051017); RnMTHFR, Rattus norvegicus MTHFR (U57049); XlMTHFR, Xenopus laevis MTHFR (BC046708); TnMTHFR, MTHFR from Tetraodon nigroviridis (CAF90576); AtMTHFR, Arabidopsis thaliana MTHFR (AF181966); ScMTHFR, Saccharomyces cerevisiae MTHFR (Z72647); EcMTHFR, E. coli MTHFR (AAN83327). Conserved serine and threonine residues in vertebrate MTHFRs are shown in red letters. Amino acids that are conserved in all MTHFR sequences are shown in green letters. The region of the human N-terminal extension that was not recovered in MALDI-MS analysis is underlined. (B) Mutant proteins were expressed in transiently transfected HEK293 cells cultured in DMEM, and the expressed human MTHFR proteins were detected by Western blotting after SDS/PAGE.