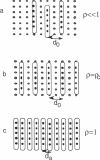
Abstract
Studies of DNA complexes with cationic liposomes are prompted by the search for nonviral DNA carriers for gene therapy. Recent experiments have identified a stable multilamellar phase in which ordered smectic layers of DNA alternate with cationic bilayers. In this paper we identify the forces governing DNA adsorption on cationic lamellae, including a membrane-induced attraction between the adsorbed DNA. Calculating the DNA interhelical spacing as a function of system composition, the model successfully explains recent surprising observations.
Full text
PDF


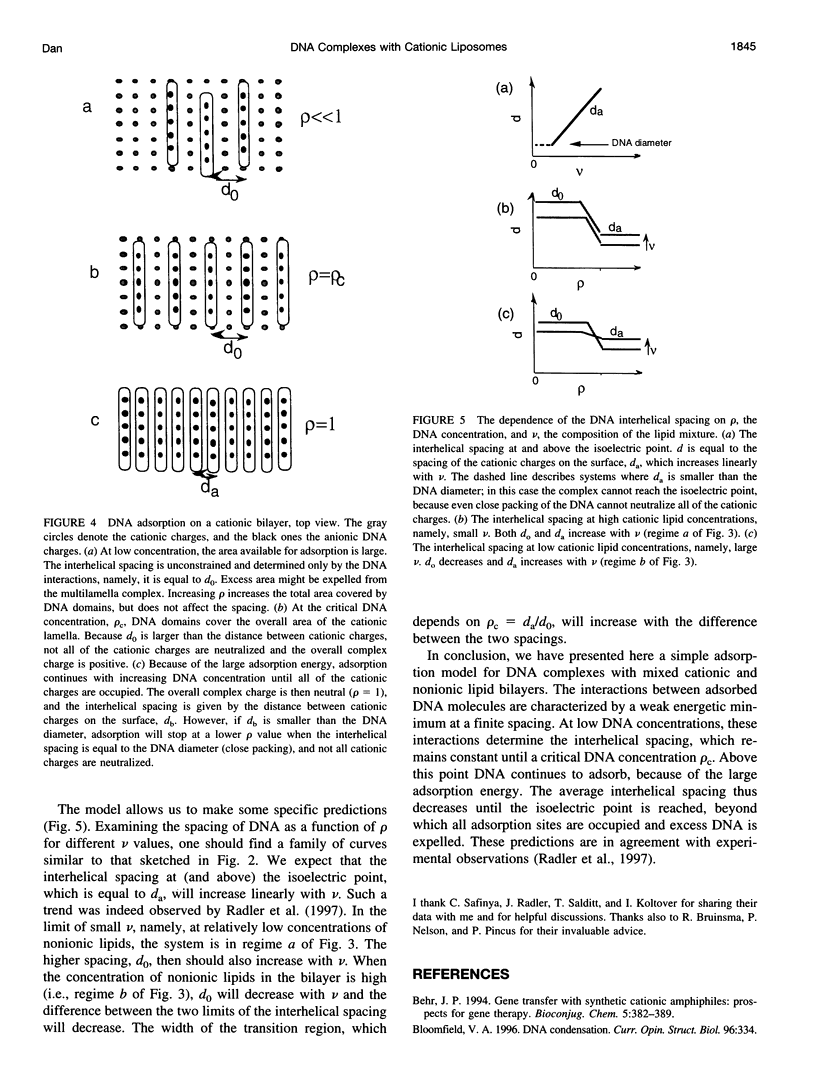

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behr J. P. Gene transfer with synthetic cationic amphiphiles: prospects for gene therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 1994 Sep-Oct;5(5):382–389. doi: 10.1021/bc00029a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield V. A. DNA condensation. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1996 Jun;6(3):334–341. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(96)80052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan N. Formation of ordered domains in membrane-bound DNA. Biophys J. 1996 Sep;71(3):1267–1272. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79326-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podgornik R., Rau D. C., Parsegian V. A. Parametrization of direct and soft steric-undulatory forces between DNA double helical polyelectrolytes in solutions of several different anions and cations. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):962–971. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80877-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rädler J. O., Koltover I., Salditt T., Safinya C. R. Structure of DNA-cationic liposome complexes: DNA intercalation in multilamellar membranes in distinct interhelical packing regimes. Science. 1997 Feb 7;275(5301):810–814. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5301.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]