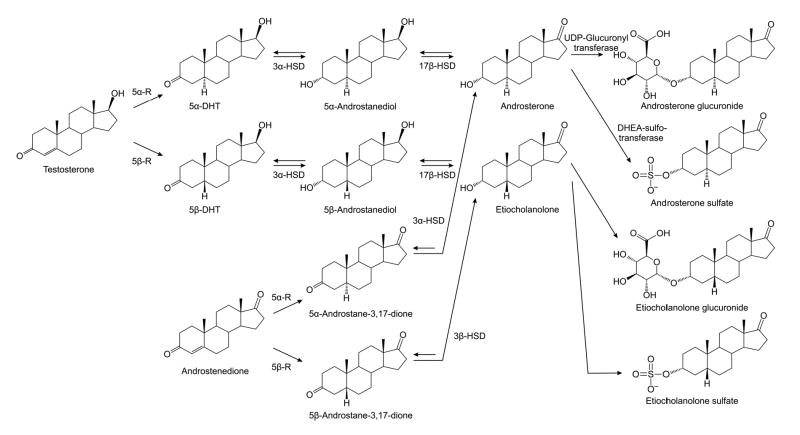
FIG. 1.
Metabolic pathways for conversion of testosterone and androstenedione to androsterone (5α-androstan-3α-ol-17-one; 5α,3α-A) and etiocholanolone (5β-androstan-3α-ol-17-one; 5β,3α-A). 5α-Reductase (5α-R) and 5β-reductase (5β-R) catalyze the rate-limiting irreversible initial steps, which are followed by sequential reductions by 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD) and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17β-HSD). 5α,3α-A and 5β,3α-A are conjugated by gucuronidation in the liver. 5α,3α-A has been identified as a substrate for human dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) sulfotransferase and some studies have indicated that 5α,3α-A sulfate may be more abundant in serum than the glucuronide (44,53).