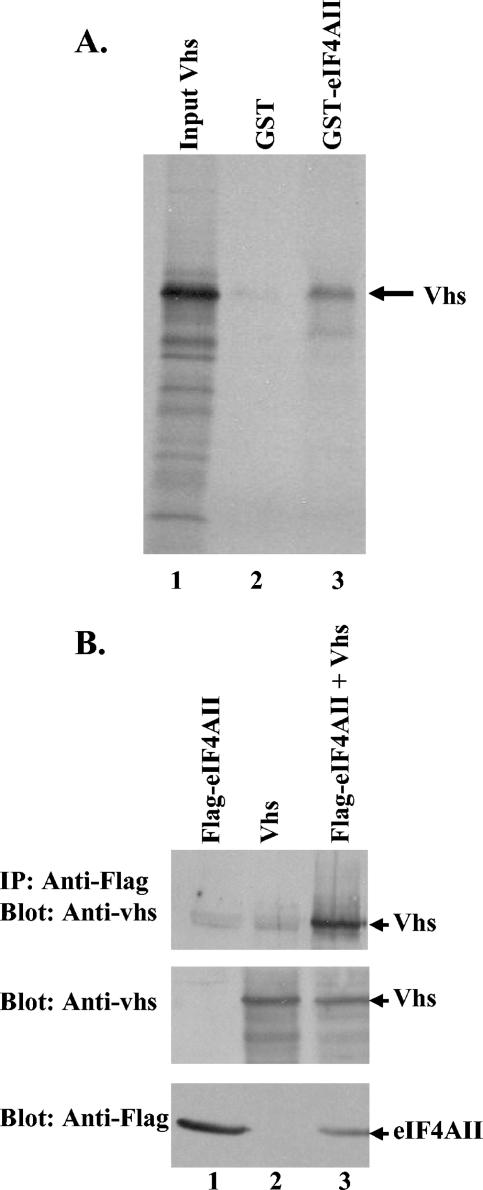
FIG. 3.
In vitro and in vivo binding of Vhs to eIF4AII. (A) Binding of Vhs to a GST-eIF4AII fusion protein. GST or a GST-eIF4AII fusion protein was produced in E. coli, bound to glutathione-Sepharose 4B, and incubated with rabbit reticulocyte lysates containing [35S]methionine-labeled in vitro-translated Vhs. Bound proteins were eluted with 10 mM glutathione and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Lanes 2 and 3 contain proteins that bound to GST-eIF4AII and GST, respectively, while lane 1 contains an aliquot of the starting material. The Vhs protein is indicated by an arrow. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of Vhs and eIF4AII from mammalian cells. CV-1 cells were infected with 5 PFU/cell of the recombinant vaccinia virus vTF7. Thirty minutes later, they were transfected with 5 μg (each) of plasmids expressing Flag-tagged eIF4AII (lane 1), the D194N allele of Vhs (lane 2), or Flag-eIF4AII and D194N Vhs (lane 3). Cell extracts were prepared 20 h after transfection, and complexes containing Flag-eIF4AII were immunoprecipitated using a Flag-specific monoclonal antibody (top). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for coprecipitated Vhs by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with a Vhs-specific rabbit antiserum. To check for protein expression, aliquots of the cell lysates were analyzed directly by Western blotting using a Vhs-specific antiserum (middle) or a Flag-specific monoclonal antibody (bottom).