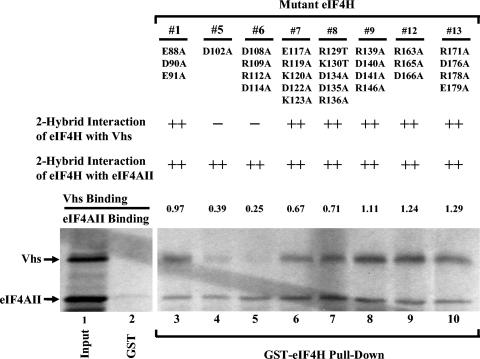
FIG. 7.
Binding of mutant eIF4H polypeptides to Vhs and eIF4AII. Eight of the mutant eIF4H polypeptides diagrammed in Fig. 6 were tested for binding to Vhs and full-length eIF4AII using the recombination-based yeast two-hybrid system and GST pull-down assays. The number of each mutant is shown at the top of the figure, just above the amino acid substitutions that each mutant contains. The second and third lines contain the results of recombination based yeast two-hybrid assays to test the interaction of the mutant eIF4H polypeptides with Vhs and eIF4AII, respectively. ++ indicates that the mutant eIF4H allele yielded a number of colonies similar to that of the wild-type eIF4H in the recombination-based two-hybrid assay; − indicates that the number of colonies was reduced at least 10 fold relative to those of wild-type eIF4H. For GST pull-down assays, full-length mutant eIF4H polypeptides were expressed as GST-eIF4H fusion proteins in E. coli, bound to glutathione-Sepharose 4B, and incubated with rabbit reticulocyte lysates containing a mixture of [35S]methionine-labeled Vhs and eIF4AII produced by in vitro transcription and translation. Bound proteins were eluted with 10 mM glutathione and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography as described in the legends to Fig. 1 and 3. The positions of Vhs and full-length eIF4AII are indicated by the arrows to the left of the gel. For each mutant, the relative amounts of bound Vhs and eIF4AII were determined by densitometric scanning of the autoradiogram and expressed as a ratio normalized to the ratio determined for wild-type eIF4H (data not shown). These ratios are indicated in line 4. Lane 1 contains an aliquot of the input mixture of Vhs and full-length eIF4AII; lane 2 contains material that bound to GST alone; lanes 3 through 10 contain material that bound to each of the mutant GST-eIF4H fusion proteins.