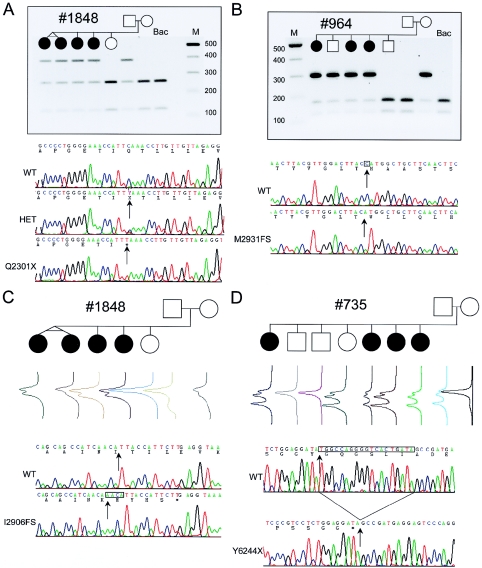
Figure 1.
Segregation of VLGR1 mutations Q2301X, M2931FS, I2906FS, and T6244X in families 735, 964, and 1848 (with USH2C). A, Paternal inheritance of Q2301X in family 1848 is shown by agarose-gel electrophoresis of exon 31 PCR product XmnI digests. Q2301X mutation is a 6901 C→T transition, 33 bp on the 3′ end of the alternate exon 31 splice donor, affecting only the VLGR1b mRNA isoform (fig. 2a). Shown here are sequence electropherograms from the heterozygous family 1848 proband (HET), an apparent Q2301X homozygote, and wild-type (WT) BAC clone RP11-29K14, with sequence and amino acid translation differences (arrows). The Q2301X homozygote was the result of a brother-sister incestuous union, whereas another singleton case was a Q2301X/occult heterozygote (data not shown; table 1). B, Maternal inheritance of M2931FS in family 964 is shown by agarose-gel electrophoresis of exon 39 PCR product NcoI digests. Sequence electropherograms of the WT and the cloned M2931FS allele show 8790delC in exon 39 (arrows). This deletion causes a 10-codon frameshift. ending with a TAG stop encoded by the last 3 bases of exon 39, affecting VLGR1b. C, Maternal inheritance of I2906FS in family 1848 by DHPLC of exon 38 PCR products. Sequence comparison of the cloned I2906FS mutation shows an 8716–17insAACA (arrows) causing a frameshift of 5 codons and ending with a TGA stop 1 bp short of the 3′ end of exon 38, affecting VLGR1b. D, Paternal inheritance of Y6244X detected by DHPLC of exon 89 PCR products. A 19-bp deletion brings a TAG stop codon immediately in-frame. Y6244X removes 63 amino acids from the COOH end of VLGR1a and VLGR1b. The putative maternal and paternal mutations in family 735 and family 964 have not been identified.