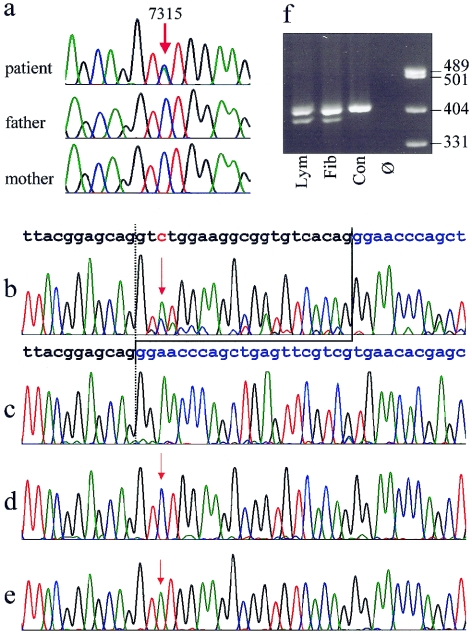
Figure 3.
a, Sequence traces from genomic DNA of the patient and her clinically normal parents, showing the heterozygous C→A exchange position, 7315, in the patient and absence of the mutation in both parents. b–e, Demonstration of the expression of two different aberrant FLNA transcripts in fibroblasts. b, Electropherogram derived from sequencing of the RT-PCR products from fibroblast mRNA, showing the presence of a shortened alternative transcript lacking 21 bases from exon 45. The normal sequence of the exons 45 and 46 are indicated above in black and blue, respectively. The position of the point mutation 7315C→A is depicted in red and marked by red arrows. Note that the T peak at position of the mutation is higher than the C representing the wild-type allele. Predominance of the mutant allele reflects the X-inactvation pattern. c–e, Sequences from different clones of the RT-PCR product cloned in E. coli. All three transcripts predicted from the sequencing results in panel b could be detected: 21-bp deletion (c), wild-type allele (d), and point mutation (e). f, Electrophoresis of a 409-bp RT-PCR fragment on a 2.5% agarose gel, showing presence of a shortened fragment in the patient's lymphocytes (lym) and fibroblasts (fib) but not in a normal male control (con). Ø = no template control.