Table 2.
Performance of Hudson’s Pairwise Composite Likelihood Method
| A. Data Simulated with Uniform Crossing Over and Uniform Conversion | |||||||
| Rate |
|||||||
| ρ | γ |
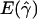 a a
|
g(γ)b | B(γ)c |
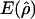 a a
|
g(ρ)b | B(ρ)c |
| 20 | 40 | 38.02 | .25 | .64 | 20.78 | .80 | .55 |
| 40 | 40 | 33.82 | .21 | .71 | 44.22 | .84 | .49 |
| 60 | 40 | 42.10 | .21 | .68 | 64.10 | .85 | .48 |
| 30 | 20 | 29.82 | .13 | .66 | 31.84 | .82 | .53 |
| 30 | 40 | 38.08 | .25 | .67 | 31.63 | .84 | .51 |
| 30 | 60 | 44.82 | .28 | .72 | 33.07 | .81 | .49 |
| B. Data Simulated with Nonuniform Crossing Over and Uniform Conversion | |||||||
| Rate |
|||||||
| ρ | γ |
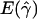 a a
|
g(γ)b | B(γ)c |
 a a
|
g(ρ)b | B(ρ)c |
| 20 | 40 | 29.01 | .26 | .73 | 21.05 | .81 | .54 |
| 40 | 40 | 23.06 | .14 | .81 | 40.71 | .83 | .56 |
| 60 | 40 | 18.43 | .17 | .85 | 58.60 | .90 | .58 |
| 30 | 20 | 14.95 | .12 | .78 | 29.17 | .83 | .59 |
| 30 | 40 | 22.55 | .21 | .80 | 30.85 | .82 | .54 |
| 30 | 60 | 36.45 | .28 | .77 | 30.94 | .83 | .55 |
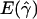 and
and 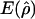 denote the averages of the MLEs of gene-conversion (
denote the averages of the MLEs of gene-conversion ( ) and crossing-over (
) and crossing-over (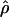 ) rates for the 500 data sets simulated at the corresponding crossing-over (ρ) and gene-conversion (γ) rate.
) rates for the 500 data sets simulated at the corresponding crossing-over (ρ) and gene-conversion (γ) rate.
g(γ) and g(ρ) denote the fraction of times 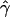 and
and 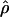 for a simulated data set is within a factor of 2 of the true γ and ρ, respectively (Wall 2000).
for a simulated data set is within a factor of 2 of the true γ and ρ, respectively (Wall 2000).
B(γ) and B(ρ)denote the fraction of times 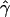 and
and  are less than their true values.
are less than their true values.
