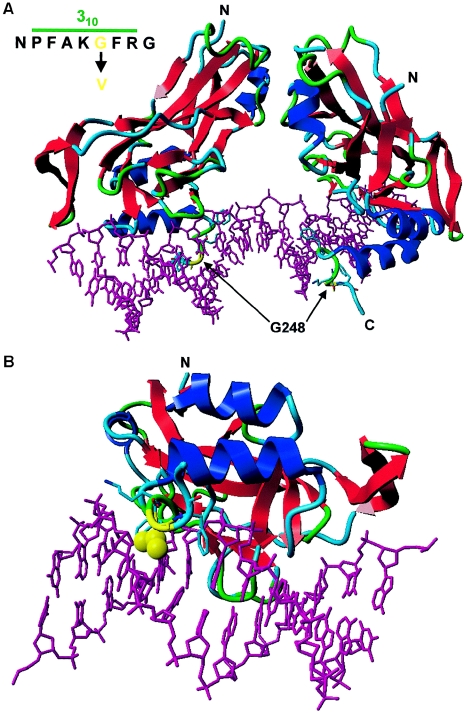
Figure 5.
Protein model of the T-box domain of TBX4, created with the help of the modelling methods described by Chinea et al. (1995) and the resolved structure of TBX3 as template (Coll et al. 2002) (Protein Data Bank). The T-box domains of TBX3 and TBX4 show a high degree of homology (80%) and identity (64%), which ensures a faithful prediction of the TBX4 structure. The 310 helical axis of the T-box domains of TBX3 and TBX4 are 100% identical. The residues of the DNA are represented as a purple stick model. Protein is shown as a ribbon model with red strands, blue helices, and green/turquoise turns and loops. The protein-DNA complex is viewed along the T-box. A, T-box dimer binding to a DNA consensus sequence. Residue G248 (yellow) is located in the C-terminal 310 helix that interacts with the DNA in the minor groove. B, View along the 310 helical axis of the T-box domain. The G248V mutation leads to the introduction of a hydrophobic side chain (yellow atoms in the ball display) that is normally absent. This likely displaces water molecules that stabilize the protein-DNA interaction through hydrogen bonding. Therefore, the G248V mutation is predicted to destabilize the TBX4-DNA interaction. Other highlighted amino acids include F245, K247, and F249 (stick representations).