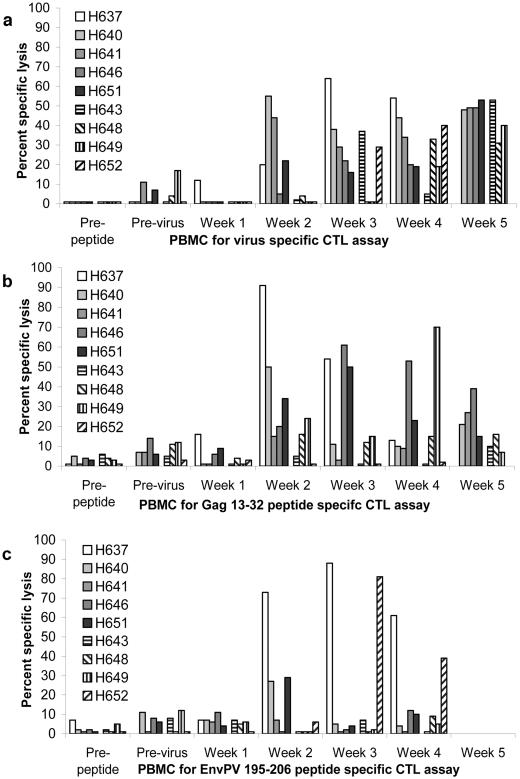
FIG. 1.
CTL activities of PBMCs from horses before immunization (prepeptide), after five lipopeptide immunizations (previrus), and following EIAVPV challenge (weeks 1 to 5). The first five horses listed in each legend (H637, H640, H641, H646, and H651) were immunized with EIAV lipopeptides, and the next four horses (H643, H648, H649, and H652) were immunized with an Anaplasma control lipopeptide. (a) EK cell targets were EIAVPV infected, and prepeptide and previrus PBMC effectors were stimulated with EIAVPV, whereas PBMCs obtained after challenge (weeks 1 to 5) were stimulated with EIAVWSU5. (b) The Gag 13-32 peptide was used to stimulate PBMCs and pulse EK cell targets. (c) The EnvPV 195-206 peptide was used to stimulate PBMCs and pulse EK cell targets. In panel a, the percent specific lysis of noninfected targets was subtracted from the percent specific lysis of infected targets; in panels b and c, the percent specific lysis of non-peptide-pulsed targets was subtracted from that of peptide-pulsed targets. The corrected specific lysis in this figure of ≥10% was considered a significant positive assay result, as these assay results were also ≥3 SEs above those for the noninfected or nonpulsed targets. Peptide targets for H637 previrus had levels of spontaneous lysis that were too high and were not used. Neither H637 PBMCs nor H652 PBMCs were available for testing at week 5 (a and b), and no assay was performed in week 5 with EnvPV 195-206 (c). The effector cell-to-target cell ratio was 20:1.