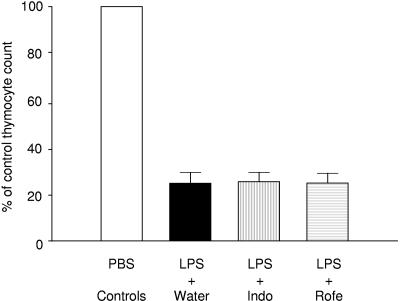
FIG. 4.
COX inhibition does not protect against LPS-induced thymocyte apoptosis. Thymocyte apoptosis was induced by injecting 50 μg of LPS in the peritoneal cavity of wild-type C57BL/6 mice. In the experimental groups, animals were treated with indomethacin (n = 7), rofecoxib (n = 5), or vehicle control (n = 12) in the drinking water beginning the day prior to LPS injection. Each experimental group had its own control, consisting of animals treated with indomethacin (n = 3), rofecoxib (n = 3), or vehicle control (n = 5) in the drinking water and injected with a similar volume of PBS. Twenty-four hours after injection, apoptotic thymocyte deletion was assessed as described in the text. The data are expressed as the percentage of the control thymocyte count (thymocyte count of experimental group divided by the mean thymocyte count of the respective PBS control and multiplied by 100). Neither indomethacin nor rofecoxib protected against the marked apoptotic thymocyte deletion induced by LPS administration.