Figure 2.
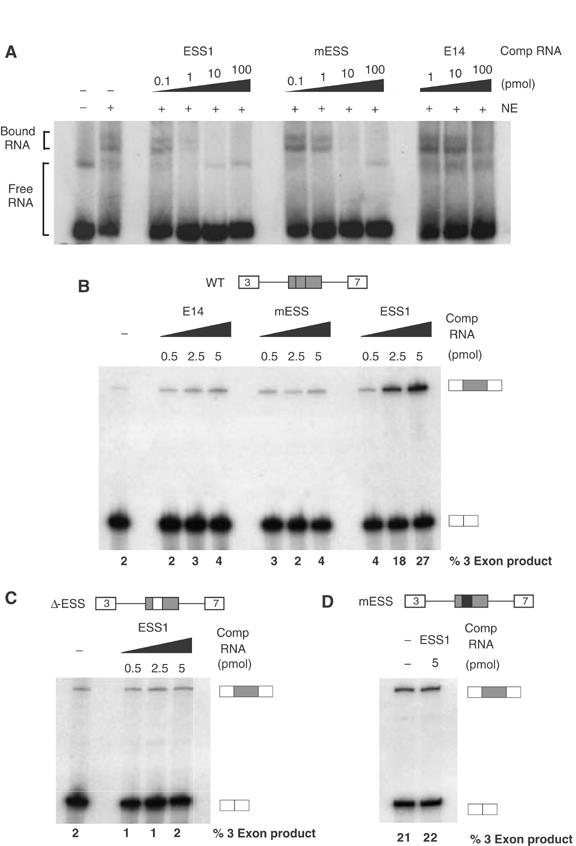
An exon-repression complex specifically associates with ESS1. (A) 32P-labeled ESS1 RNA (0.1 pmol) was incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of nuclear extract from unstimulated JSL1 cells and resolved on a native gel to observe free and bound RNA species. Unlabeled competitor RNA was also added to the reactions as indicated. (B) In all, 1 fmol unlabeled, capped RNA derived from a minigene containing WT CD45 variable exon 4, flanked by constitutive exons 3 and 7, was incubated in nuclear extract from unstimulated JSL1 cells in the presence or absence of exogenous competitor RNA. The resulting spliced products were then assayed by RT–PCR, as done for RNA derived from cells. Quantitation of the % 3-exon product is the average of at least four experiments with a standard deviation of <20% for all values given. (C) RNA derived from a CD45 exon 4 minigene in which the ESS1 has been deleted and replaced with heterologous sequence was spliced in the same assay as used for (B). (D) In vitro splicing as in panel B of RNA derived from a CD45 exon 4 minigene in which the ESS1 has been mutated to the ‘mESS' sequence shown in Figure 1C.
