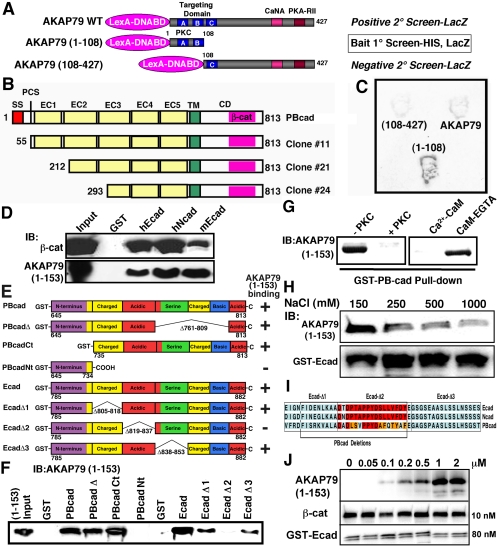
Figure 1.
Identification of an interaction between AKAP79/150 and cadherins. (A) Diagram showing the AKAP79 baits used in positive [AKAP79(1-108) and AKAP79WT] and negative [AKAP79(108-427)] yeast two-hybrid screens of a rat brain cDNA library. Locations of three basic regions (A–C) within the targeting domain and PKC-, CaNA-, and PKA-RII-anchoring sites are indicated. (B) Primary structures of Gal4-cDNA PBcad clones identified as interacting with the AKAP79(1-108) bait. The extracellular domain (EC), transmembrane domain (TM), cytoplasmic domain (CD), signal sequence (SS), proteolytic cleavage site (PCS), Ca2+-adhesion repeats (EC1–5), and β-cat are indicated. (C) Representative yeast two-hybrid βgal filter assays for interactions of the indicated baits with PBcad Clone#24. (D) Five hundred nanograms of purified AKAP79(1-153)-His6 tagged fragment or β-cat was assayed for cadherin CD binding in vitro by precipitation with 5 μg of GST (negative control) and 5 μg of GST-CD fusions for human Ecad (hEcad) and Ncad (hNcad) and mouse Ecad (mEcad) followed by immunoblotting (IB:). (E) Diagram showing the primary structures of PBcad and Ecad deletions used to map the AKAP79 binding site (not to scale). Previously delineated (Kaplan et al., 2001) subregions within the cadherin CD that are rich in charged, acidic, serine, or basic residues are indicated. AKAP79(1-153) binding results (shown in F) are summarized by a + or –sign. (F) Representative immunoblots showing AKAP79(1-153) binding activity for the PBcad and Ecad-CD constructs diagramed in E. GST-fusion constructs were present at equal levels (5 μg), except Ecad-Δ2 and Ecad-Δ3 were present at fivefold higher levels, suggesting reduced binding for Ecad-Δ3. (G) PKC phosphorylation or preincubation of 1 μg of AKAP79(1-153) with 1 μM Ca2+-CaM, but not CaM plus EGTA, prevented GST-PBcad pulldown. (H) High salt concentrations (250–1000 mM) inhibit AKAP79(1-153) binding to GST-Ecad. (I) Amino acid sequence alignment of human Ecad, Ncad, and rat PBcad showing regions within the β-cat binding domain that are necessary for AKAP79 binding. Identical residues are shown in red and conservative substitutions in orange. (J) Immunoblots showing saturable binding of AKAP79(1-153) (0.05–2 μM) to a fixed amount of GST-Ecad (80 nM) with equal amounts of β-cat (10 nM). Both AKAP79(1-153) and β-cat are pulled down, even in the presence of a large molar excess of AKAP present (∼200-fold over β-cat).