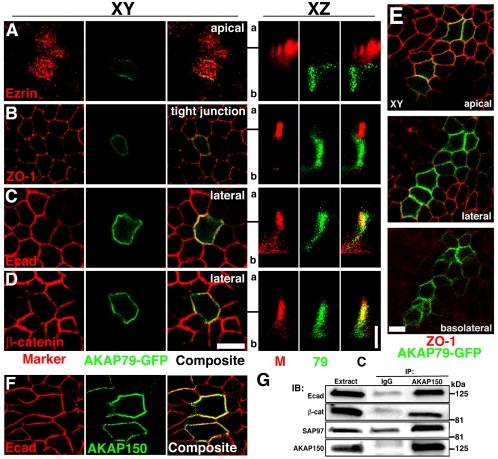
Figure 4.
Polarized localization of AKAP79-GFP and association of AKAP150 with E-cadherin at lateral membranes of MDCK epithelial cells. Lack of colocalization of AKAP79-GFP (green) with apical marker ezrin (79, red) (A) and tight junction marker ZO-1 (M, red) (B). Colocalization (yellow) of AKAP79-GFP (79, green) with lateral membrane Ecad (M, red) (C) and β-cat (M, red) (D). (A–D) Right-hand panels show vertical xz line-scan sections from apical (a) to basolateral (b) for the same cells shown in the left-hand xy panels (y location in xy plane relative to the xz scan is indicated by a black line). (E) Apical, lateral, and basolateral xy sections showing AKAP79-GFP (green) basolateral membrane localization relative to tight junction ZO-1 (red). (F) Lateral membrane (xy) colocalization (yellow) of AKAP150 (green) with Ecad (red). (G) Coimmunoprecipitation of Ecad, β-cat, and SAP97(hDlg) with 5 μg of anti-AKAP150 but not nonimmune IgG from ∼3 mg of transfected MDCK cell lysates. Bars, 10 μm for xy sections, 5 μm for xz sections. Note: We are unable to detect expression of any endogenous canine AKAP protein with our antibodies to human AKAP79 or rat AKAP150.