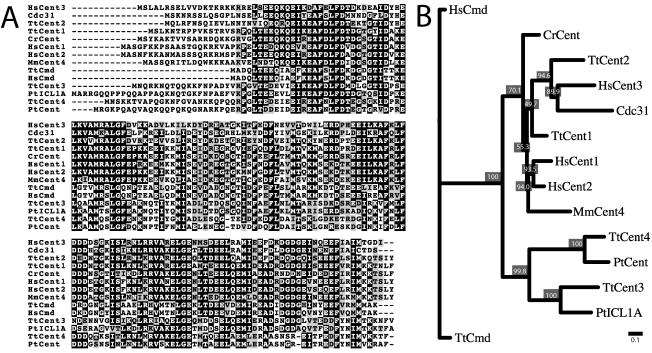
Figure 1.
Comparison of centrins from different organisms. Tt, T. thermophila; Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Cr, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Pt, P. tetraurelia; Cdc31 from S. cerevisiae; Cmd, calmodulin. (A) Twelve representative centrins were aligned along with two calmodulin proteins. Residues where 50% or more are identical between the proteins are shaded black, and residues where 50% or more are similar are shaded gray. (B) The centrin and calmodulin sequences were subjected to phylogenetic analysis using the Neighbor-Joining method; 1000 replicates were performed, and a representative unrooted tree is displayed as a dendogram. Bootstrap values are displayed as percentages at each node and indicate how often the separation delineated by the branching occurred. Bar = 0.1 substitutions per one amino acid (see Materials and Methods).