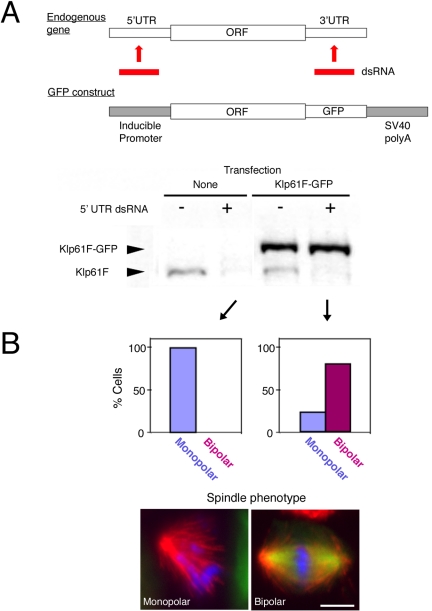
Figure 1.
Rescue assay in S2 cells. (A) Top, schematic representation of a rescue assay in S2 cells. dsRNA targeting 5′UTR or 3′UTR is used for RNAi knockdown of an endogenous gene. An exogenous gene lacking UTR sequences, such as GFP-fusion gene shown here, can be expressed and is resistant to the dsRNA. Bottom, immunoblotting with anti-Klp61F against control untransfected cells and a Klp61F-GFP–expressing cell line after 5′UTR RNAi (lanes 2 and 4) or no RNA treatment (lanes 1 and 3). 5′UTR dsRNA specifically knocked down endogenous Klp61F but not the expressed Klp61F-GFP. (B) The RNAi rescue assay shows that Klp61F-GFP is functional. Top, phenotypic analysis shows that monopolar spindles were observed after RNAi of untransfected cells (left), whereas bipolar spindles were found predominantly in the Klp61F-GFP–expressing cell line (right). Note that some Klp61F-GFP cells (22%) do not express GFP, and those cells formed monopolar spindles. Bottom, immunofluorescence examples of a monopolar spindle after 5′UTR-based RNAi (left) and a bipolar spindle after rescued by Klp61F-GFP expression (right). Blue, DNA; green, GFP; and red, tubulin. Bar, 5 μm.