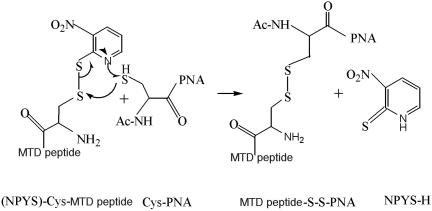
Scheme 1.
Mechanism of conjugation chemistry for PNA–MTD peptides. The peptide moiety has cysteine at its N-terminus and it is activated by incorporating an -NPYS group. The PNA has a terminal cysteine at its 5′ end. In a redox reaction, the S-S linkage is formed which is stable in cell culture media but is easily degraded in the reductive intracellular environment. This degradation is critical for the peptide moiety to complete its task as a transporting vector, releasing the PNA inside the cell. Upon reduction of the disulfide bond, the PNA is released and migrates towards its target.