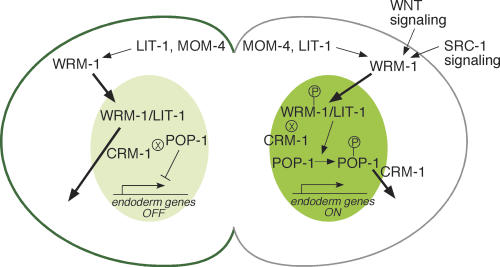
Figure 4.
A model for asymmetric localization of WRM-1::GFP. Schematic diagram of polarity signaling in the EMS cell at telophase. WRM-1 protein is retained in the posterior E nucleus (dark green) and exported from the MS nucleus (lighter green). Conversely, WRM-1 is preferentially retained, in a MOM-5/Fz-dependent manner, at the anterior cortex (dark-green line) and released at the posterior cortex (gray line). Arrows and bars between signaling components depict activating and inhibitory genetic interactions, respectively. Signaling from Wnt and Src leads to phosphorylation of WRM-1 and POP-1 (indicated by the P within a circle). The ⊗ symbol adjacent to WRM-1 (in E) and POP-1 (in MS) indicates reduced CRM-1-dependent export. Bold arrows indicate nuclear entry or export.