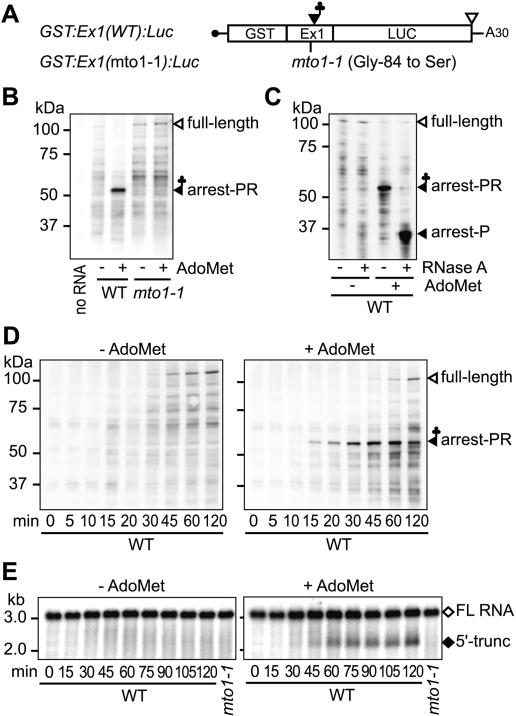
Figure 1.
Translation elongation arrest and RNA degradation. (A) Schematic representation of GST:Ex1:Luc RNA. (B,C) Immunoblot analysis. GST:Ex1(WT):Luc RNA or GST:Ex1(mto1-1): Luc RNA was translated for 30 min in the presence (+) or absence (-) of 1 mM AdoMet. The translation products were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-GST antibody. In C, the WT samples were treated with RNase A as indicated before separation by SDS-PAGE. The 106-kDa full-length translation product (full-length), the 55-kDa AdoMet-dependent peptidyl-RNA (arrest-PR), and the AdoMet-dependent band shifted by the RNase A treatment (arrest-P) are marked. (D,E) Time course analyses. GST:Ex1(WT):Luc RNA was translated in the presence (right) or absence (left) of AdoMet. Aliquots were withdrawn at the indicated time points and subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-GST antibody (D) or Northern blot analysis with LUC 3′ probe (E). The full-length RNA (FL RNA) and the 5′-truncated RNA (5′-trunc) are marked in E. Representative results of duplicate to triplicate experiments are shown.