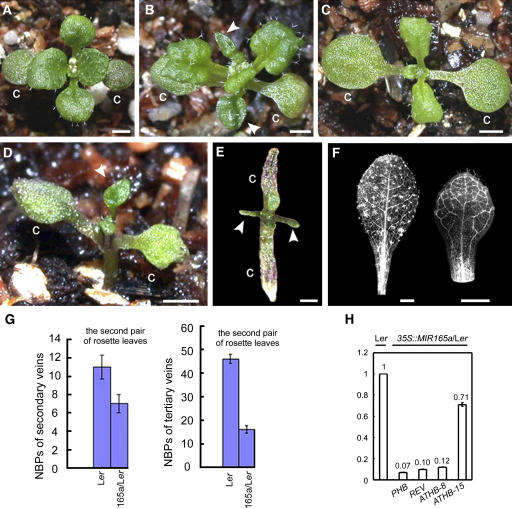
Figure 10.
Phenotypes of 35S:MIR165a Transgenic Plants.
(A) A 35S:MIR165a/Ler seedling, showing small and round leaves with margins slightly curled downward. C, cotyledon.
(B) A 35S:MIR165a/as2-101 seedling with ruffled leaf surfaces. Arrowheads indicate the lotus leaves.
(C) A 35S:MIR165a/rdr6-3 seedling. First-pair rosette leaves resemble those of the as2-101 mutant plants.
(D) A 35S:MIR165a/rdr6-3 transgenic plant showing a lotus leaf structure (arrowhead).
(E) A 35S:MIR165a/rdr6-3 transgenic plant displaying severe phenotypes with abaxialized needle-like leaves (arrowheads).
(F) Comparison of venation between wild-type (left) and 35S:MIR165a/Ler (right) leaves, showing that venation of the 35S:MIR165a/Ler transgenic line was simplified. Bars = 1 mm in (A) to (F).
(G) Quantitative analyses of NBPs in wild-type and 35S:MIR165a/Ler transgenic plants.
(H) Real-time RT-PCR to examine steady state levels of mRNA of class III HD-ZIP genes in wild-type and 35S:MIR165a/Ler plants. Bars show standard error.