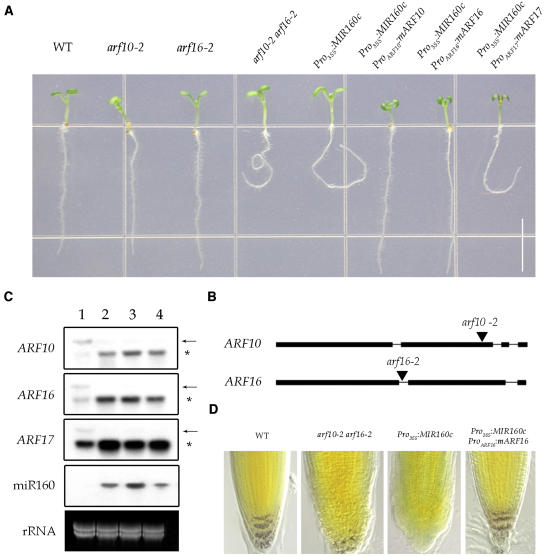
Figure 2.
ARF10 and ARF16 Control Root Cap Formation.
(A) Five-day-old seedlings showing agravitropic root growth (arf10-2 arf16-2, Pro35S:MIR160c, and Pro35S:MIR160c ProARF17:mARF17) and rescue by expressing ARF10 or ARF16 (Pro35S:MIR160c ProARF10:mARF10, Pro35S:MIR160c ProARF16:mARF16). ProARF17:mARF17 failed to rescue the gravitropism. WT, wild type. Bar = 0.5 cm.
(B) Schemes of T-DNA insertion mutants of arf10-2 and arf16-2. Black boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. Triangles indicate the T-DNA insertion site.
(C) RNA gel blot of the ARF transcripts in 20-d-old wild-type (lane 1), Pro35S:MIR160a (lane 2), Pro35S:MIR160b (lane 3), and Pro35S:MIR160c (lane 4) plants. In plants ectopically overexpressing miR160, most of the target transcripts were decreased and the level of cleaved products was increased. Arrows and asterisks indicate the full-length and 3′ cleaved products of each mRNA, respectively.
(D) Root tip and starch granules (stained purple) of 5-d-old seedlings.