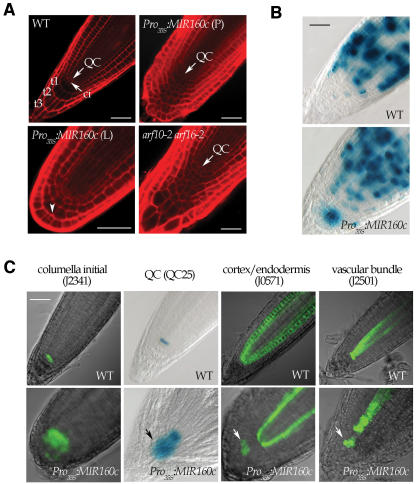
Figure 3.
Disruption of ARF10 and ARF16 Results in Defects in Differentiation and Patterning of Root Distal Cells.
(A) Compared with the wild type, the 5-d-old Pro35S:MIR160c and arf10-2 arf16-2 seedlings displayed uncontrolled division of undifferentiated cells in the distal regions of both primary (P) and lateral (L) roots. In Pro35S:MIR160c (L), the arrowhead indicates aberrantly dividing cells. Cell outlines were stained by propidium iodide (red). ci, columella initial; QC, quiescent center; t1 to t3, three columella cell tiers in wild-type root cap. Bars = 50 μm in all panels.
(B) Expression of the mitotic marker Procyc1At:CDB-GUS in wild-type (top) and Pro35S:MIR160c (bottom) roots. In Pro35S:MIR160c, GUS activity was extended down to the root distal region.
(C) Expression of GFP- and GUS-based markers in wild-type (top row) and Pro35S:MIR160c (bottom row) root tips. Shown are marker lines J2341 for columella initials, QC25 for QC, J0517 for cortex/endodermis, and J2501 for the vascular bundle. Arrows indicates the enlarged expression domain of the QC marker in Pro35S:MIR160c root.